Real Assets
Visualizing the Metals You Can Buy with $1,000

Visualizing the Metals you can Buy with $1,000
For millennia people have purchased and relied on metals for decorative and industrial uses, figuring out their values based on their practical applications and visual luster.
Today, precious and industrial metals markets quote figures in millions and billions as they exchange thousands of ounces, with varying densities and values of metals making it difficult to compare them.
Using price data from TradingEconomics, this graphic visualizes how much of each metal you can buy for $1,000 so you can see just how much, or how little, of each metal you get for your money.
How we Value Precious and Industrial Metals
Characterized by their natural shine, metals are valued using the two key principles of rarity and their industrial uses, with unique properties such as their appearance or cultural significance also affecting their value.
- Rarity: A more scarce metal or resource will often have a higher value than one which is more abundant.
- For example, while there are an estimated 2.1 billion tonnes of identified copper deposits, there are only 57,000 tonnes of underground gold reserves. While copper is valued at $0.24 per troy ounce, gold is worth around $1,815 per troy ounce.
- Industrial uses: Metals which are needed for important industrial processes will often have a high demand from manufacturers, increasing their valuation.
- For example, for most of its history cobalt was used decoratively for its striking blue color and for the creation of superalloys and steel products. However, when it was recently discovered that cobalt could be a key component in lithium-ion batteries for EVs, demand for cobalt surged sending its price from around $23,000 per tonne to more than $90,000 per tonne at one point.
Along with these two primary factors, unique properties and historical uses can also affect a metal’s valuation.
Former monetary metals like gold and silver are still sought after by investors for their potential ability to retain value over time compared to today’s fiat currencies. Meanwhile, platinum’s durability, resistance to tarnishing, and its bright white color makes it highly sought after for jewelry, raising the demand and value of the precious metal.
Getting Less for More: Comparing Metal Density
A key factor that determines the volume of a metal you get for a certain price is also the metal’s density. Precious metals tend to be more dense than industrial metals, with sometimes more than double the density depending on the specific metals compared.
As seen in the graphic above, $1,000 worth of highly dense metals like gold (19.32 g/cm³), iridium (22.56 g/cm³), and osmium (22.59 g/cm³) amount to small cubes less than a centimeter across. Meanwhile, $1,000 of a less dense (and also less valuable) metal like aluminum with a density of only 2.7 g/cm³ yields a large cube nearly two feet tall.
To put these densities in comparison, if gold had the same density as aluminum, its cube on the graphic above would be more than seven times larger.
While it’s impossible to directly compare the value of each metal’s industrial uses and applications, seeing just how much (or how little) of a metal you get for $1,000 can give some perspective to their value.
Real Assets
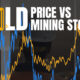
Charted: The Value Gap Between the Gold Price and Gold Miners
While gold prices hit all-time highs, gold mining stocks have lagged far behind.

Gold Price vs. Gold Mining Stocks
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on Apple or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Although the price of gold has reached new record highs in 2024, gold miners are still far from their 2011 peaks.
In this graphic, we illustrate the evolution of gold prices since 2000 compared to the NYSE Arca Gold BUGS Index (HUI), which consists of the largest and most widely held public gold production companies. The data was compiled by Incrementum AG.
Mining Stocks Lag Far Behind
In April 2024, gold reached a new record high as Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell signaled policymakers may delay interest rate cuts until clearer signs of declining inflation materialize.
Additionally, with elections occurring in more than 60 countries in 2024 and ongoing conflicts in Ukraine and Gaza, central banks are continuing to buy gold to strengthen their reserves, creating momentum for the metal.
Traditionally known as a hedge against inflation and a safe haven during times of political and economic uncertainty, gold has climbed over 11% so far this year.
According to Business Insider, gold miners experienced their best performance in a year in March 2024. During that month, the gold mining sector outperformed all other U.S. industries, surpassing even the performance of semiconductor stocks.
Still, physical gold has outperformed shares of gold-mining companies over the past three years by one of the largest margins in decades.
| Year | Gold Price | NYSE Arca Gold BUGS Index (HUI) |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $2,062.92 | $243.31 |
| 2022 | $1,824.32 | $229.75 |
| 2021 | $1,828.60 | $258.87 |
| 2020 | $1,895.10 | $299.64 |
| 2019 | $1,523.00 | $241.94 |
| 2018 | $1,281.65 | $160.58 |
| 2017 | $1,296.50 | $192.31 |
| 2016 | $1,151.70 | $182.31 |
| 2015 | $1,060.20 | $111.18 |
| 2014 | $1,199.25 | $164.03 |
| 2013 | $1,201.50 | $197.70 |
| 2012 | $1,664.00 | $444.22 |
| 2011 | $1,574.50 | $498.73 |
| 2010 | $1,410.25 | $573.32 |
| 2009 | $1,104.00 | $429.91 |
| 2008 | $865.00 | $302.41 |
| 2007 | $836.50 | $409.37 |
| 2006 | $635.70 | $338.24 |
| 2005 | $513.00 | $276.90 |
| 2004 | $438.00 | $215.33 |
| 2003 | $417.25 | $242.93 |
| 2002 | $342.75 | $145.12 |
| 2001 | $276.50 | $65.20 |
| 2000 | $272.65 | $40.97 |
Among the largest companies on the NYSE Arca Gold BUGS Index, Colorado-based Newmont has experienced a 24% drop in its share price over the past year. Similarly, Canadian Barrick Gold also saw a decline of 6.5% over the past 12 months.
Real Assets
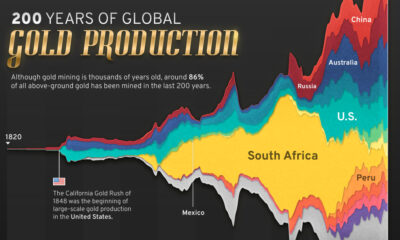
200 Years of Global Gold Production, by Country
Global gold production has grown exponentially since the 1800s, with 86% of all above-ground gold mined in the last 200 years.
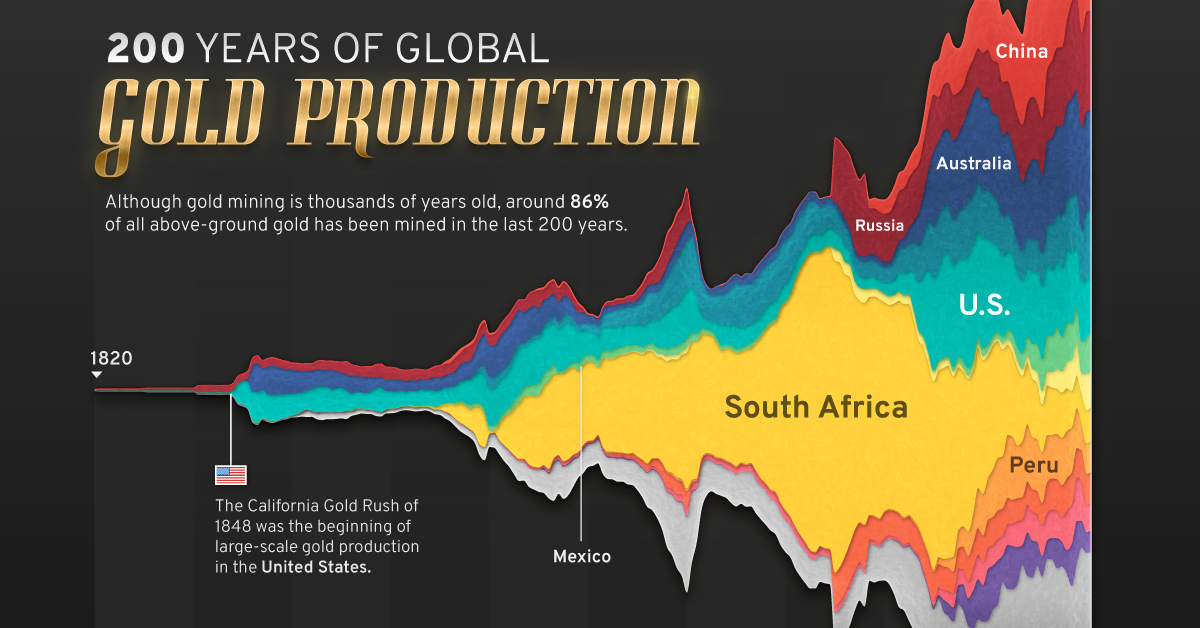
Visualizing Global Gold Production Over 200 Years
Although the practice of gold mining has been around for thousands of years, it’s estimated that roughly 86% of all above-ground gold was extracted in the last 200 years.
With modern mining techniques making large-scale production possible, global gold production has grown exponentially since the 1800s.
The above infographic uses data from Our World in Data to visualize global gold production by country from 1820 to 2022, showing how gold mining has evolved to become increasingly global over time.
A Brief History of Gold Mining
The best-known gold rush in modern history occurred in California in 1848, when James Marshall discovered gold in Sacramento Valley. As word spread, thousands of migrants flocked to California in search of gold, and by 1855, miners had extracted around $2 billion worth of gold.
The United States, Australia, and Russia were (interchangeably) the three largest gold producers until the 1890s. Then, South Africa took the helm thanks to the massive discovery in the Witwatersrand Basin, now regarded today as one of the world’s greatest ever goldfields.
South Africa’s annual gold production peaked in 1970 at 1,002 tonnes—by far the largest amount of gold produced by any country in a year.
With the price of gold rising since the 1980s, global gold production has become increasingly widespread. By 2007, China was the world’s largest gold-producing nation, and today a significant quantity of gold is being mined in over 40 countries.
The Top Gold-Producing Countries in 2022
Around 31% of the world’s gold production in 2022 came from three countries—China, Russia, and Australia, with each producing over 300 tonnes of the precious metal.
| Rank | Country | 2022E Gold Production, tonnes | % of Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 🇨🇳 China | 330 | 11% |
| #2 | 🇷🇺 Russia | 320 | 10% |
| #3 | 🇦🇺 Australia | 320 | 10% |
| #4 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 220 | 7% |
| #5 | 🇺🇸 United States | 170 | 5% |
| #6 | 🇲🇽 Mexico | 120 | 4% |
| #7 | 🇰🇿 Kazakhstan | 120 | 4% |
| #8 | 🇿🇦 South Africa | 110 | 4% |
| #9 | 🇵🇪 Peru | 100 | 3% |
| #10 | 🇺🇿 Uzbekistan | 100 | 3% |
| #11 | 🇬🇭 Ghana | 90 | 3% |
| #12 | 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 70 | 2% |
| - | 🌍 Rest of the World | 1,030 | 33% |
| - | World Total | 3,100 | 100% |
North American countries Canada, the U.S., and Mexico round out the top six gold producers, collectively making up 16% of the global total. The state of Nevada alone accounted for 72% of U.S. production, hosting the world’s largest gold mining complex (including six mines) owned by Nevada Gold Mines.
Meanwhile, South Africa produced 110 tonnes of gold in 2022, down by 74% relative to its output of 430 tonnes in 2000. This long-term decline is the result of mine closures, maturing assets, and industrial conflict, according to the World Gold Council.
Interestingly, two smaller gold producers on the list, Uzbekistan and Indonesia, host the second and third-largest gold mining operations in the world, respectively.
The Outlook for Global Gold Production
As of April 25, gold prices were hovering around the $2,000 per ounce mark and nearing all-time highs. For mining companies, higher gold prices can mean more profits per ounce if costs remain unaffected.
According to the World Gold Council, mined gold production is expected to increase in 2023 and could surpass the record set in 2018 (3,300 tonnes), led by the expansion of existing projects in North America. The chances of record mine output could be higher if gold prices continue to increase.
-

 Electrification3 years ago
Electrification3 years agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe Key Minerals in an EV Battery
-

 Real Assets3 years ago
Real Assets3 years agoThe World’s Top 10 Gold Mining Companies
-

 Misc3 years ago
Misc3 years agoAll the Metals We Mined in One Visualization
-
 Electrification3 years ago
Electrification3 years agoThe Biggest Mining Companies in the World in 2021
-

 Energy Shift2 years ago
Energy Shift2 years agoWhat Are the Five Major Types of Renewable Energy?
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoMapped: Solar Power by Country in 2021
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe World’s Largest Nickel Mining Companies