Technology Metals
How Strong Are Rare Earth Magnets?
How Strong Are Rare Earth Magnets?
Magnets are an integral part of many technologies and appliances in the 21st century.
From tiny fridge magnets that hold to-do lists to powerful ones that create magnetic fields for electricity generation from wind turbines, there are many different types of magnets.
The world’s strongest magnets, also known as rare earth magnets, are made by alloying certain rare earth elements with other materials.
But just how strong are rare earth magnets, and what makes them so powerful?
Measuring Magnet Strength
The above infographic uses data from First4Magnets to compare the strength of magnets. But before looking at the strongest magnets, it’s essential to understand how to measure magnetic strength.
The maximum energy product, measured in mega-gauss-oersteds (MGOe), is one of the primary indicators of magnetic strength. It is a multiplication of two measurements: a magnet’s remanence and its coercivity.
- Remanence:
To become magnets, ferromagnetic substances need to enter the magnetic field of an existing magnet. Remanence, measured in Gauss, is the magnetism left in the magnet after removing the external magnetic field. - Coercivity:
Coercivity is the energy required to bring a magnetic material’s magnetism down to zero. Measured in oersteds, it essentially captures the magnetic material’s resistance to demagnetization.
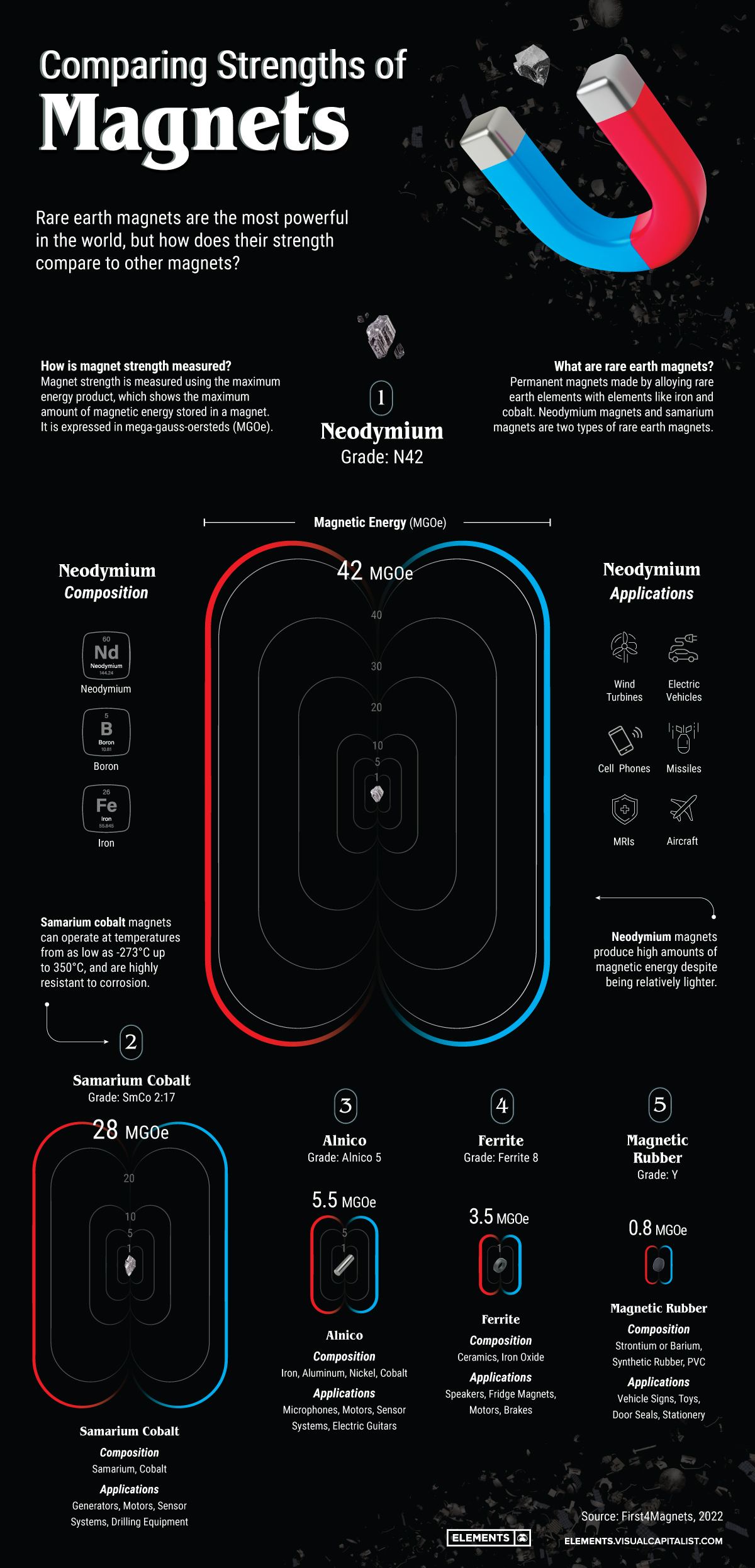
The Strength of Rare Earth Magnets
Each magnet has a grade, which typically denotes its strength. For example, a neodymium magnet of grade N42 has a strength of 42MGOe.
To put the power of two common rare earth magnet grades into perspective, here’s how their strength compares with common grades of other permanent magnets:
| Magnet (Grade) | Composition | Maximum Energy Product (MGOe) |
|---|---|---|
| Neodymium (N42) | Neodymium, iron, boron | 42 |
| Samarium Cobalt (SmCo 2:17) | Samarium, cobalt | 28 |
| Alnico (Alnico-5) | Iron, aluminum, nickel, cobalt | 5.5 |
| Ferrite (Ferrite-8) | Ceramics, iron oxide | 3.5 |
| Magnetic rubber (Grade Y) | Strontium or barium, synthetic rubber, PVC | 0.8 |
Note: While the N42 neodymium magnet is used more commonly, the strongest available magnet is of grade N52.
Neodymium and samarium—two of the 17 rare earth elements—are ferromagnetic, meaning that they have inherent magnetic properties and can be magnetized. These metals are first mined, refined, and then combined with materials like iron, boron, and/or cobalt to make the strongest magnetic alloys.
Neodymium magnets are typically composed of one-third neodymium, along with iron and boron. Some of the neodymium in magnets can be replaced with praseodymium, another rare earth material. For this reason, neodymium magnets are also known as NdPr magnets.
Due to their strength, neodymium magnets have found their way into various technologies, from phones and laptops to motors in electric vehicles. In fact, according to Adamas Intelligence, 90% of all EV motors use NdPr magnets. Because these magnets also offer relatively high strength for a smaller size, they are also the predominant choice for wind turbines, reducing turbine weight significantly.
Samarium-cobalt magnets exhibit exceptional resistance to extreme temperatures. These magnets can operate from temperatures as low as -270℃ up to 350℃ and are also highly resistant to corrosion. Consequently, they have important applications in harsh marine environments and technologies with high operating temperatures.
The Demand for Neodymium Magnets
Global EV sales more than doubled last year, up from around 3 million cars in 2020 to 6.6 million in 2021. Similarly, renewable energy is expanding at a record pace, with capacity installations in 2022 set to break the record set the previous year.
With that in mind, it’s no surprise that the demand for rare earth magnets is expected to increase. Neodymium magnet consumption is forecasted to grow from more than 100,000 tonnes in 2020 to 300,000 tonnes by 2035, with EVs and wind turbines driving growth.
However, the supply chain of neodymium magnets remains a concern with China controlling the majority of rare earth extraction, refining, and downstream magnet production.
Energy Shift
China Dominates the Supply of U.S. Critical Minerals List
China was the world’s leading producer of 30 out of 50 entries on the U.S. critical minerals list, according to the U.S. Geological Survey.
China Dominates the Supply of U.S. Critical Minerals List
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Most countries have, for many decades, kept a record of their own critical minerals list.
For example, the U.S., drew up a list of “war minerals” during World War I, containing important minerals which could not be found and produced in abundance domestically. They included: tin, nickel, platinum, nitrates and potash.
Since then, as the economy has grown and innovated, critical mineral lists have expanded considerably. The Energy Act of 2020 defines a critical mineral as:
“A non-fuel mineral or mineral material essential to the economic or national security of the U.S., whose supply chains are vulnerable to disruption.” — Energy Act, 2020.
Currently there are 50 entries on this list and the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) estimates that China is the leading producer for 30 of them. From USGS data, we visualize China’s share of U.S. imports for 10 critical minerals.
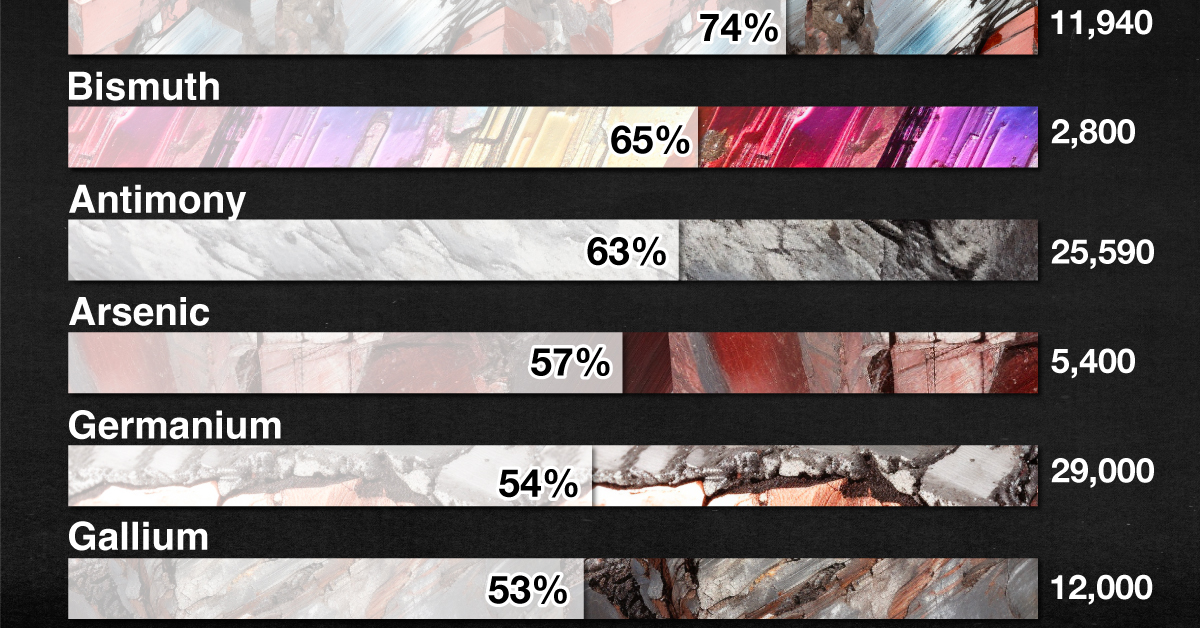
What Key Critical Minerals Does the U.S. Import From China?
The U.S. is 100% import-reliant for its supply of yttrium, with China responsible for 94% of U.S. imports of the metal from 2018 to 2021.
A soft silvery metal, yttrium is used as an additive for alloys, making microwave filters for radars, and as a catalyst in ethylene polymerization—a key process in making certain kinds of plastic.
China is a major supplier of the following listed critical minerals to the U.S.
| Critical Mineral | China's Share of U.S. Imports | U.S. Imports (Tonnes) | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yttrium | 94% | 1,000 | Catalyst, Microwave filters |
| Rare Earths | 74% | 11,940 | Smartphones, Cameras |
| Bismuth | 65% | 2,800 | Metallurgy |
| Antimony | 63% | 25,590 | Batteries |
| Arsenic | 57% | 5,400 | Semiconductors |
| Germanium | 54% | 29,000 | Chips, Fiber optics |
| Gallium | 53% | 12,000 | Chips, Fiber optics |
| Barite | 38% | 2,300 | Hydrocarbon production |
| Graphite (natural) | 33% | 82,000 | Batteries, Lubricants |
| Tungsten | 29% | 14,000 | Metallurgy |
Note: China’s share of U.S. critical minerals imports is based on average imports from 2018 to 2021.
Meanwhile, the U.S. also imports nearly three-quarters of its rare earth compounds and metals demand from China. Rare earth elements—so called since they are not found in easily-mined, concentrated clusters—are a collection of 15 elements on the periodic table, known as the lanthanide series.
Rare earths are used in smartphones, cameras, hard disks, and LEDs but also, crucially, in the clean energy and defense industries.
Does China’s Dominance of U.S. Critical Minerals Supply Matter?
The USGS estimates that China could potentially disrupt the global rare earth oxide supply by cutting off 40–50% production, impacting suppliers of advanced components used in U.S. defense systems.
A version of this sort of trade warfare is already playing out. Earlier this year, China implemented export controls on germanium and gallium. The U.S. relies on China for around 54% of its demand for both minerals, used for producing chips, solar panels, and fiber optics.
China’s controls were seen as a retaliation against the U.S. which has restricted the supply of chips, chip design software, and lithography machines to Chinese companies.
Technology Metals
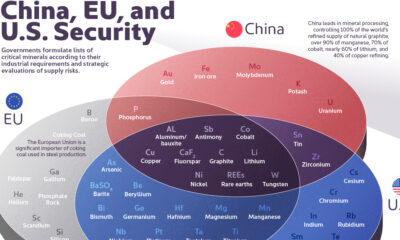
The Critical Minerals to China, EU, and U.S. National Security
Ten materials, including cobalt, lithium, graphite, and rare earths, are deemed critical by all three.
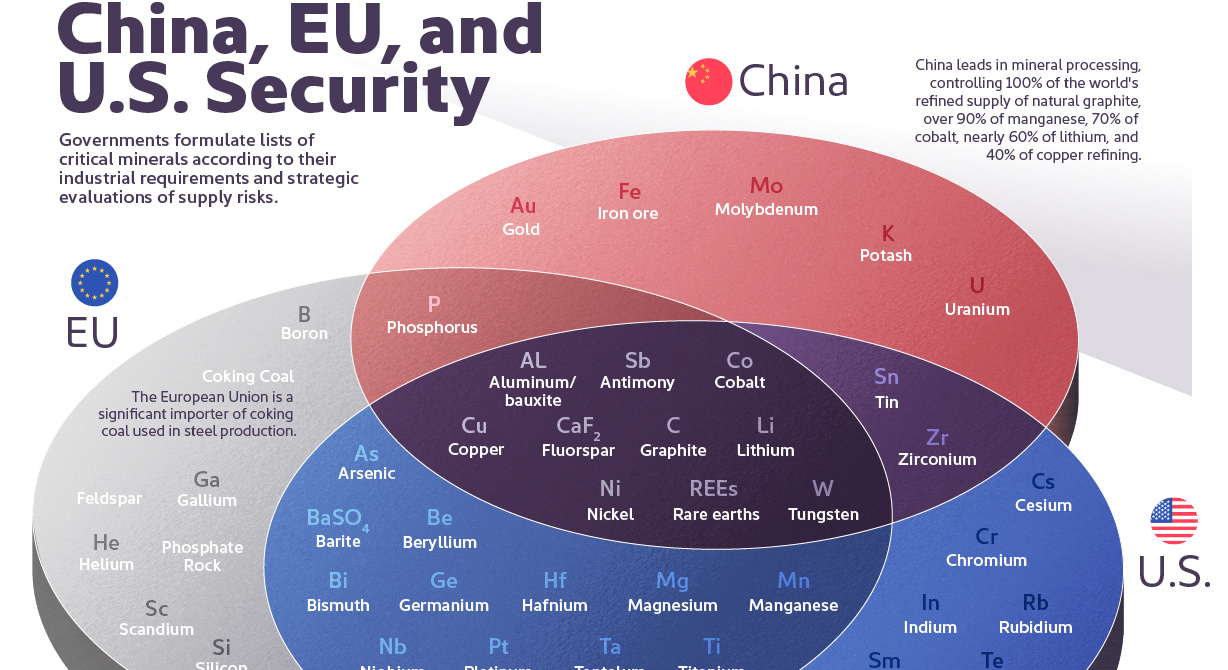
The Critical Minerals to China, EU, and U.S. Security
Governments formulate lists of critical minerals according to their industrial requirements and strategic evaluations of supply risks.
Over the last decade, minerals like nickel, copper, and lithium have been on these lists and deemed essential for clean technologies like EV batteries and solar and wind power.
This graphic uses IRENA and the U.S. Department of Energy data to identify which minerals are essential to China, the United States, and the European Union.
What are Critical Minerals?
There is no universally accepted definition of critical minerals. Countries and regions maintain lists that mirror current technology requirements and supply and demand dynamics, among other factors.
These lists are also constantly changing. For example, the EU’s first critical minerals list in 2011 featured only 14 raw materials. In contrast, the 2023 version identified 34 raw materials as critical.
One thing countries share, however, is the concern that a lack of minerals could slow down the energy transition.
With most countries committed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, the total mineral demand from clean energy technologies is expected to double by 2040.
U.S. and EU Seek to Reduce Import Reliance on Critical Minerals
Ten materials feature on critical material lists of both the U.S., the EU, and China, including cobalt, lithium, graphite, and rare earths.
| Mineral / Considered Critical | 🇺🇸 U.S. | 🇪🇺 EU | 🇨🇳 China |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum/ bauxite | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Antimony | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Cobalt | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Copper | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Fluorspar | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Graphite | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Lithium | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Nickel | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Rare earths | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Tungsten | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Arsenic | Yes | Yes | No |
| Barite | Yes | Yes | No |
| Beryllium | Yes | Yes | No |
| Bismuth | Yes | Yes | No |
| Germanium | Yes | Yes | No |
| Hafnium | Yes | Yes | No |
| Magnesium | Yes | Yes | No |
| Manganese | Yes | Yes | No |
| Niobium | Yes | Yes | No |
| Platinum | Yes | Yes | No |
| Tantalum | Yes | Yes | No |
| Titanium | Yes | Yes | No |
| Vanadium | Yes | Yes | No |
| Tin | Yes | No | Yes |
| Zirconium | Yes | No | Yes |
| Phosphorus | No | Yes | Yes |
| Cesium | Yes | No | No |
| Chromium | Yes | No | No |
| Indium | Yes | No | No |
| Rubidium | Yes | No | No |
| Samarium | Yes | No | No |
| Tellurium | Yes | No | No |
| Zinc | Yes | No | No |
| Boron | No | Yes | No |
| Coking Coal | No | Yes | No |
| Feldspar | No | Yes | No |
| Gallium | No | Yes | No |
| Helium | No | Yes | No |
| Phosphate Rock | No | Yes | No |
| Scandium | No | Yes | No |
| Silicon | No | Yes | No |
| Strontium | No | Yes | No |
| Gold | No | No | Yes |
| Iron ore | No | No | Yes |
| Molybdenum | No | No | Yes |
| Potash | No | No | Yes |
| Uranium | No | No | Yes |
Despite having most of the same materials found in the U.S. or China’s list, the European list is the only one to include phosphate rock. The region has limited phosphate resources (only produced in Finland) and largely depends on imports of the material essential for manufacturing fertilizers.
Coking coal is also only on the EU list. The material is used in the manufacture of pig iron and steel. Production is currently dominated by China (58%), followed by Australia (17%), Russia (7%), and the U.S. (7%).
The U.S. has also sought to reduce its reliance on imports. Today, the country is 100% import-dependent on manganese and graphite and 76% on cobalt.
After decades of sourcing materials from other countries, the U.S. local production of raw materials has become extremely limited. For instance, there is only one operating nickel mine (primary) in the country, the Eagle Mine in Michigan. Likewise, the country only hosts one lithium source in Nevada, the Silver Peak Mine.
China’s Dominance
Despite being the world’s biggest carbon polluter, China is the largest producer of most of the world’s critical minerals for the green revolution.
China produces 60% of all rare earth elements used as components in high-technology devices, including smartphones and computers. The country also has a 13% share of the lithium production market. In addition, it refines around 35% of the world’s nickel, 58% of lithium, and 70% of cobalt.
Among some of the unique materials on China’s list is gold. Although gold is used on a smaller scale in technology, China has sought gold for economic and geopolitical factors, mainly to diversify its foreign exchange reserves, which rely heavily on the U.S. dollar.
Analysts estimate China has bought a record 400 tonnes of gold in recent years.
China has also slated uranium as a critical mineral. The Chinese government has stated it intends to become self-sufficient in nuclear power plant capacity and fuel production for those plants.
According to the World Nuclear Association, China aims to produce one-third of its uranium domestically.
-

 Electrification3 years ago
Electrification3 years agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe Key Minerals in an EV Battery
-

 Real Assets3 years ago
Real Assets3 years agoThe World’s Top 10 Gold Mining Companies
-

 Misc3 years ago
Misc3 years agoAll the Metals We Mined in One Visualization
-
 Electrification3 years ago
Electrification3 years agoThe Biggest Mining Companies in the World in 2021
-

 Energy Shift2 years ago
Energy Shift2 years agoWhat Are the Five Major Types of Renewable Energy?
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoMapped: Solar Power by Country in 2021
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe World’s Largest Nickel Mining Companies