Electrification
Visualizing the World’s Largest Hydroelectric Dams
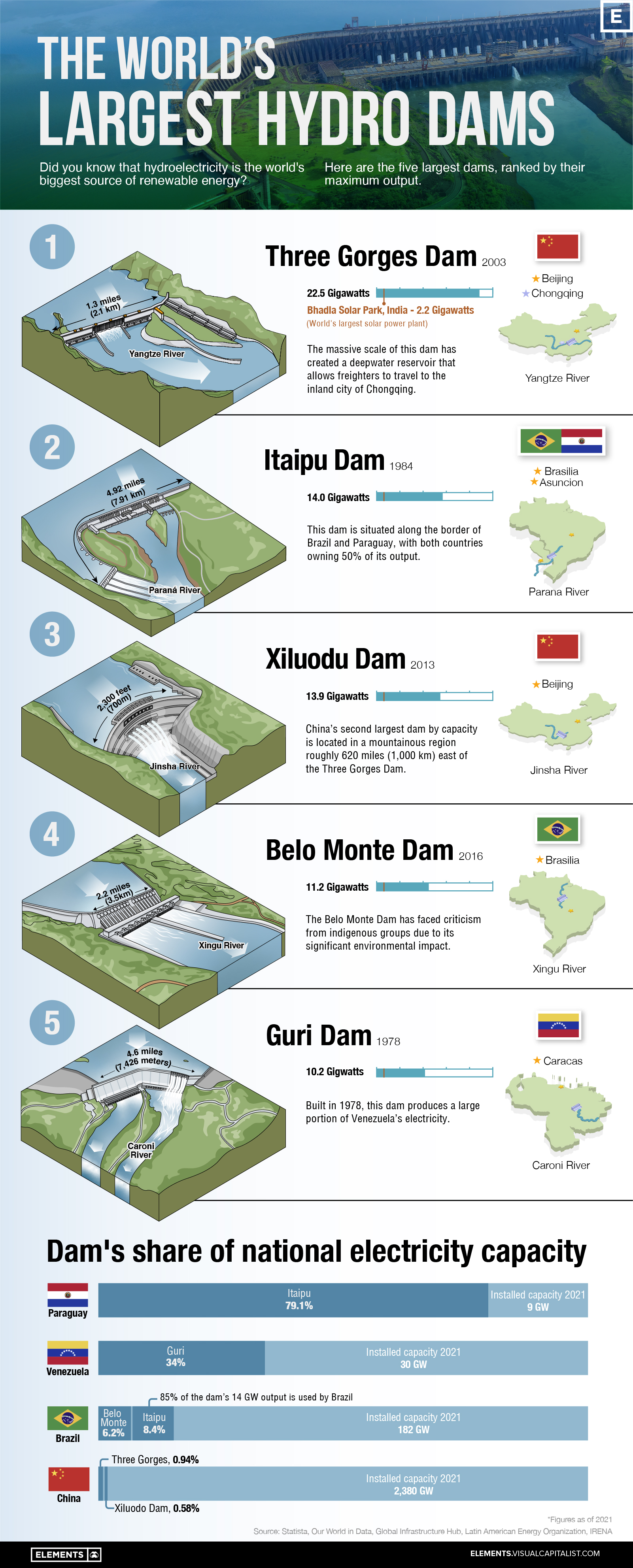
Visualizing the World’s Largest Hydroelectric Dams
Did you know that hydroelectricity is the world’s biggest source of renewable energy? According to recent figures from the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), it represents 40% of total capacity, ahead of solar (28%) and wind (27%).
This type of energy is generated by hydroelectric power stations, which are essentially large dams that use the water flow to spin a turbine. They can also serve secondary functions such as flow monitoring and flood control.
To help you learn more about hydropower, we’ve visualized the five largest hydroelectric dams in the world, ranked by their maximum output.
Overview of the Data
The following table lists key information about the five dams shown in this graphic, as of 2021. Installed capacity is the maximum amount of power that a plant can generate under full load.
| Country | Dam | River | Installed Capacity (gigawatts) | Dimensions (meters) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 🇨🇳 China | Three Gorges Dam | Yangtze River | 22.5 | 181 x 2,335 |
| 🇧🇷 Brazil / 🇵🇾 Paraguay | Itaipu Dam | Parana River | 14.0 | 196 x 7,919 |
| 🇨🇳 China | Xiluodu Dam | Jinsha River | 13.9 | 286 x 700 |
| 🇧🇷 Brazil | Belo Monte Dam | Xingu River | 11.2 | 90 X 3,545 |
| 🇻🇪 Venezuela | Guri Dam | Caroni River | 10.2 | 162 x 7,426 |
At the top of the list is China’s Three Gorges Dam, which opened in 2003. It has an installed capacity of 22.5 gigawatts (GW), which is close to double the second-place Itaipu Dam.
In terms of annual output, the Itaipu Dam actually produces about the same amount of electricity. This is because the Parana River has a low seasonal variance, meaning the flow rate changes very little throughout the year. On the other hand, the Yangtze River has a significant drop in flow for several months of the year.
For a point of comparison, here is the installed capacity of the world’s three largest solar power plants, also as of 2021:
- Bhadla Solar Park, India: 2.2 GW
- Hainan Solar Park, China: 2.2 GW
- Pavagada Solar Park, India: 2.1 GW
Compared to our largest dams, solar plants have a much lower installed capacity. However, in terms of cost (cents per kilowatt-hour), the two are actually quite even.
Closer Look: Three Gorges Dam
The Three Gorges Dam is an engineering marvel, costing over $32 billion to construct. To wrap your head around its massive scale, consider the following facts:
- The Three Gorges Reservoir (which feeds the dam) contains 39 trillion kg of water (42 billion tons)
- In terms of area, the reservoir spans 400 square miles (1,045 square km)
- The mass of this reservoir is large enough to slow the Earth’s rotation by 0.06 microseconds
Of course, any man-made structure this large is bound to have a profound impact on the environment. In a 2010 study, it was found that the dam has triggered over 3,000 earthquakes and landslides since 2003.
The Consequences of Hydroelectric Dams
While hydropower can be cost-effective, there are some legitimate concerns about its long-term sustainability.
For starters, hydroelectric dams require large upstream reservoirs to ensure a consistent supply of water. Flooding new areas of land can disrupt wildlife, degrade water quality, and even cause natural disasters like earthquakes.
Dams can also disrupt the natural flow of rivers. Other studies have found that millions of people living downstream from large dams suffer from food insecurity and flooding.
Whereas the benefits have generally been delivered to urban centers or industrial-scale agricultural developments, river-dependent populations located downstream of dams have experienced a difficult upheaval of their livelihoods.
– Richter, B.D. et al. (2010)
Perhaps the greatest risk to hydropower is climate change itself. For example, due to the rising frequency of droughts, hydroelectric dams in places like California are becoming significantly less economical.
Electrification
Charted: 4 Reasons Why Lithium Could Be the Next Gold Rush
Visual Capitalist has partnered with EnergyX to show why drops in prices and growing demand may make now the right time to invest in lithium.
4 Reasons Why You Should Invest in Lithium
Lithium’s importance in powering EVs makes it a linchpin of the clean energy transition and one of the world’s most precious minerals.
In this graphic, Visual Capitalist partnered with EnergyX to explore why now may be the time to invest in lithium.
1. Lithium Prices Have Dropped
One of the most critical aspects of evaluating an investment is ensuring that the asset’s value is higher than its price would indicate. Lithium is integral to powering EVs, and, prices have fallen fast over the last year:
| Date | LiOH·H₂O* | Li₂CO₃** |
|---|---|---|
| Feb 2023 | $76 | $71 |
| March 2023 | $71 | $61 |
| Apr 2023 | $43 | $33 |
| May 2023 | $43 | $33 |
| June 2023 | $47 | $45 |
| July 2023 | $44 | $40 |
| Aug 2023 | $35 | $35 |
| Sept 2023 | $28 | $27 |
| Oct 2023 | $24 | $23 |
| Nov 2023 | $21 | $21 |
| Dec 2023 | $17 | $16 |
| Jan 2024 | $14 | $15 |
| Feb 2024 | $13 | $14 |
Note: Monthly spot prices were taken as close to the 14th of each month as possible.
*Lithium hydroxide monohydrate (MB-LI-0033)
**Lithium carbonate (MB-LI-0029)
2. Lithium-Ion Battery Prices Are Also Falling
The drop in lithium prices is just one reason to invest in the metal. Increasing economies of scale, coupled with low commodity prices, have caused the cost of lithium-ion batteries to drop significantly as well.
In fact, BNEF reports that between 2013 and 2023, the price of a Li-ion battery dropped by 82%.
| Year | Price per KWh |
|---|---|
| 2023 | $139 |
| 2022 | $161 |
| 2021 | $150 |
| 2020 | $160 |
| 2019 | $183 |
| 2018 | $211 |
| 2017 | $258 |
| 2016 | $345 |
| 2015 | $448 |
| 2014 | $692 |
| 2013 | $780 |
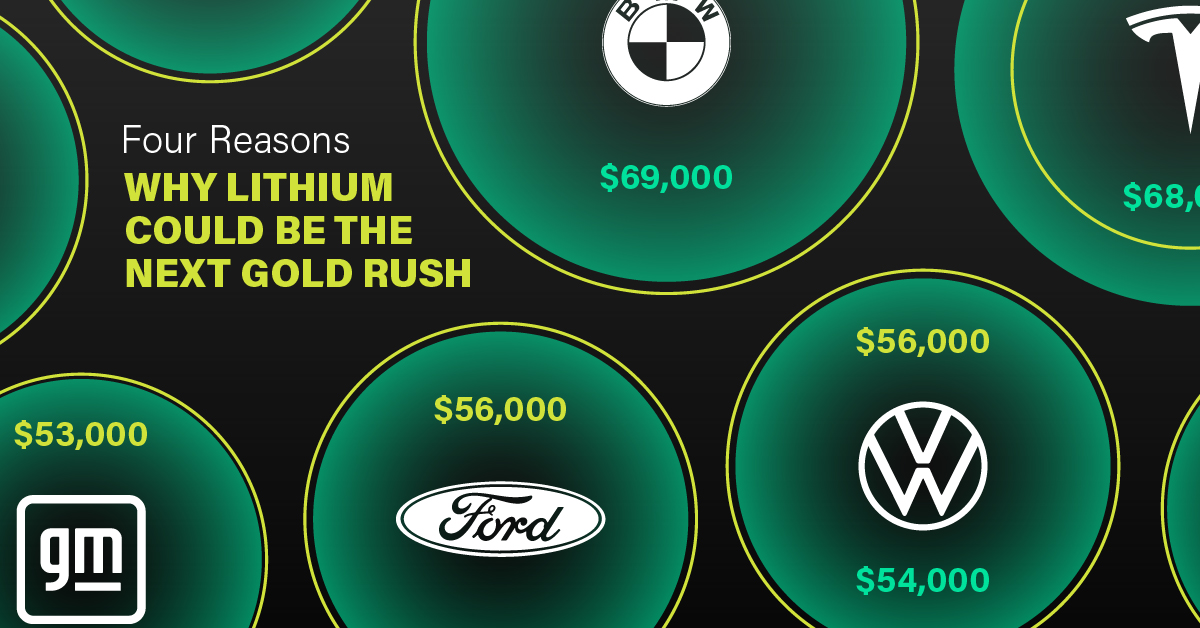
3. EV Adoption is Sustainable
One of the best reasons to invest in lithium is that EVs, one of the main drivers behind the demand for lithium, have reached a price point similar to that of traditional vehicle.
According to the Kelly Blue Book, Tesla’s average transaction price dropped by 25% between 2022 and 2023, bringing it in line with many other major manufacturers and showing that EVs are a realistic transport option from a consumer price perspective.
| Manufacturer | September 2022 | September 2023 |
|---|---|---|
| BMW | $69,000 | $72,000 |
| Ford | $54,000 | $56,000 |
| Volkswagon | $54,000 | $56,000 |
| General Motors | $52,000 | $53,000 |
| Tesla | $68,000 | $51,000 |
4. Electricity Demand in Transport is Growing
As EVs become an accessible transport option, there’s an investment opportunity in lithium. But possibly the best reason to invest in lithium is that the IEA reports global demand for the electricity in transport could grow dramatically by 2030:
| Transport Type | 2022 | 2025 | 2030 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buses 🚌 | 23,000 GWh | 50,000 GWh | 130,000 GWh |
| Cars 🚙 | 65,000 GWh | 200,000 GWh | 570,000 GWh |
| Trucks 🛻 | 4,000 GWh | 15,000 GWh | 94,000 GWh |
| Vans 🚐 | 6,000 GWh | 16,000 GWh | 72,000 GWh |
The Lithium Investment Opportunity
Lithium presents a potentially classic investment opportunity. Lithium and battery prices have dropped significantly, and recently, EVs have reached a price point similar to other vehicles. By 2030, the demand for clean energy, especially in transport, will grow dramatically.
With prices dropping and demand skyrocketing, now is the time to invest in lithium.
EnergyX is poised to exploit lithium demand with cutting-edge lithium extraction technology capable of extracting 300% more lithium than current processes.

Electrification
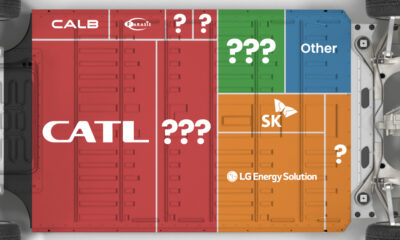
Ranked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
Asia dominates this ranking of the world’s largest EV battery manufacturers in 2023.
The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Despite efforts from the U.S. and EU to secure local domestic supply, all major EV battery manufacturers remain based in Asia.
In this graphic we rank the top 10 EV battery manufacturers by total battery deployment (measured in megawatt-hours) in 2023. The data is from EV Volumes.
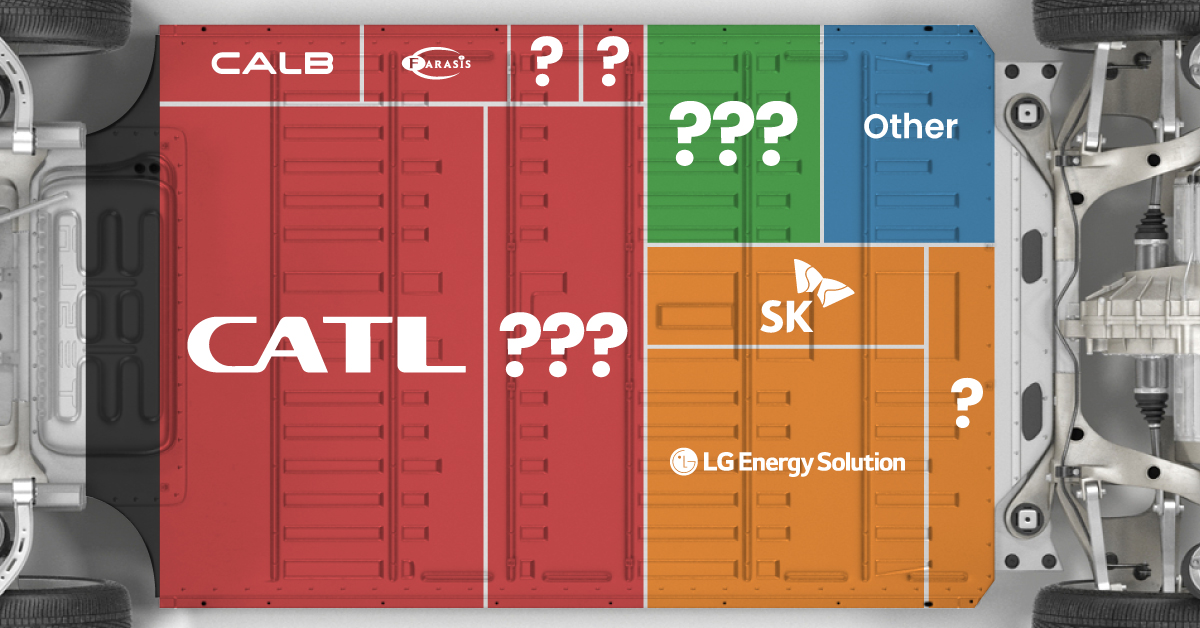
Chinese Dominance
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL) has swiftly risen in less than a decade to claim the title of the largest global battery group.
The Chinese company now has a 34% share of the market and supplies batteries to a range of made-in-China vehicles, including the Tesla Model Y, SAIC’s MG4/Mulan, and Li Auto models.
| Company | Country | 2023 Production (megawatt-hour) | Share of Total Production |
|---|---|---|---|
| CATL | 🇨🇳China | 242,700 | 34% |
| BYD | 🇨🇳China | 115,917 | 16% |
| LG Energy Solution | 🇰🇷Korea | 108,487 | 15% |
| Panasonic | 🇯🇵Japan | 56,560 | 8% |
| SK On | 🇰🇷Korea | 40,711 | 6% |
| Samsung SDI | 🇰🇷Korea | 35,703 | 5% |
| CALB | 🇨🇳China | 23,493 | 3% |
| Farasis Energy | 🇨🇳China | 16,527 | 2% |
| Envision AESC | 🇨🇳China | 8,342 | 1% |
| Sunwoda | 🇨🇳China | 6,979 | 1% |
| Other | - | 56,040 | 8% |
In 2023, BYD surpassed LG Energy Solution to claim second place. This was driven by demand from its own models and growth in third-party deals, including providing batteries for the made-in-Germany Tesla Model Y, Toyota bZ3, Changan UNI-V, Venucia V-Online, as well as several Haval and FAW models.
The top three battery makers (CATL, BYD, LG) collectively account for two-thirds (66%) of total battery deployment.
Once a leader in the EV battery business, Panasonic now holds the fourth position with an 8% market share, down from 9% last year. With its main client, Tesla, now effectively sourcing batteries from multiple suppliers, the Japanese battery maker seems to be losing its competitive edge in the industry.
Overall, the global EV battery market size is projected to grow from $49 billion in 2022 to $98 billion by 2029, according to Fortune Business Insights.
-

 Electrification3 years ago
Electrification3 years agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe Key Minerals in an EV Battery
-

 Real Assets3 years ago
Real Assets3 years agoThe World’s Top 10 Gold Mining Companies
-

 Misc3 years ago
Misc3 years agoAll the Metals We Mined in One Visualization
-
 Electrification3 years ago
Electrification3 years agoThe Biggest Mining Companies in the World in 2021
-

 Energy Shift2 years ago
Energy Shift2 years agoWhat Are the Five Major Types of Renewable Energy?
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoMapped: Solar Power by Country in 2021
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe World’s Largest Nickel Mining Companies