Energy Shift
Mapped: Asia’s Biggest Sources of Electricity by Country
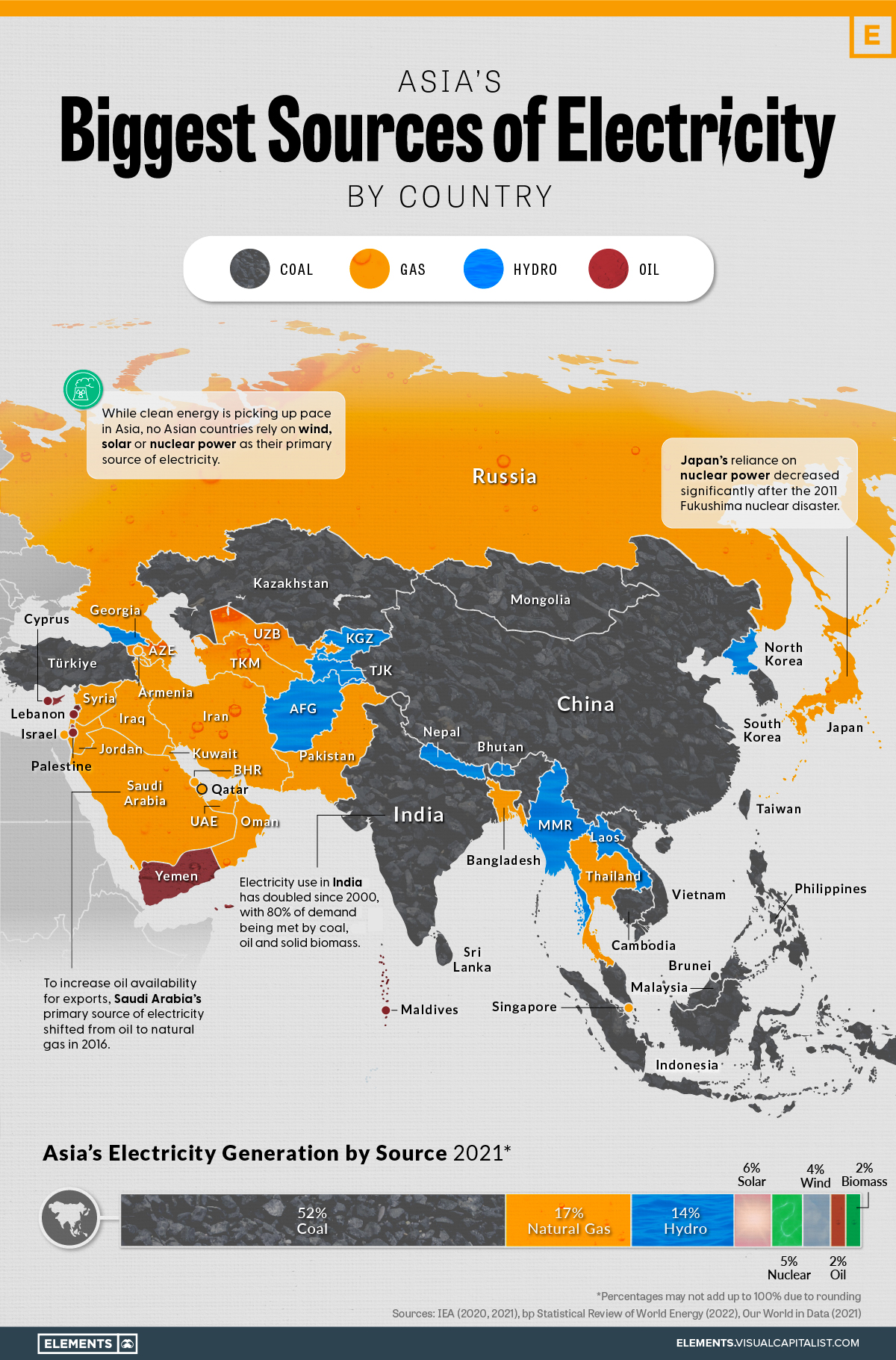
Mapped: Asia’s Biggest Sources of Electricity by Country
The International Energy Agency (IEA) predicts that Asia will account for half of the world’s electricity consumption by 2025, with one-third of global electricity being consumed in China.
To explore how this growing electricity demand is currently being met, the above graphic maps out Asia’s main sources of electricity by country, using data from the BP Statistical Review of World Energy and the IEA.
A Coal-Heavy Electricity Mix
Although clean energy has been picking up pace in Asia, coal currently makes up more than half of the continent’s electricity generation.
No Asian countries rely on wind, solar, or nuclear energy as their primary source of electricity, despite the combined share of these sources doubling over the last decade.
| % of total electricity mix, 2011 | % of total electricity mix, 2021 | |
|---|---|---|
| Coal | 55% | 52% |
| Natural Gas | 19% | 17% |
| Hydro | 12% | 14% |
| Nuclear | 5% | 5% |
| Wind | 1% | 4% |
| Solar | 0% | 4% |
| Oil | 6% | 2% |
| Biomass | 1% | 2% |
| Total Electricity Generated | 9,780 terawatt-hours | 15,370 terawatt-hours |
The above comparison shows that the slight drops in the continent’s reliance on coal, natural gas, and oil in the last decade have been absorbed by wind, solar, and hydropower. The vast growth in total electricity generated, however, means that a lot more fossil fuels are being burned now (in absolute terms) than at the start of the last decade, despite their shares dropping.
Following coal, natural gas comes in second place as Asia’s most used electricity source, with most of this demand coming from the Middle East and Russia.
Zooming in: China’s Big Electricity Demand
While China accounted for just 5% of global electricity demand in 1990, it is en route to account for 33% by 2025. The country is already the largest electricity producer in the world by far, annually generating nearly double the electricity produced by the second largest electricity producer in the world, the United States.
With such a large demand, the current source of China’s electricity is worthy of consideration, as are its plans for its future electricity mix.
Currently, China is one of the 14 Asian countries that rely on coal as its primary source of electricity. In 2021, the country drew 62% of its electricity from coal, a total of 5,339 TWh of energy. To put that into perspective, this is approximately three times all of the electricity generated in India in the same year.
Following coal, the remainder of China’s electricity mix is as follows.
| Source | % of total electricity mix (China, 2021) |
|---|---|
| Coal | 62% |
| Hydropower | 15% |
| Wind | 8% |
| Nuclear | 5% |
| Solar | 4% |
| Natural Gas | 3% |
| Biomass | 2% |
Despite already growing by 1.5x in the last decade, China’s demand for electricity is still growing. Recent developments in the country’s clean energy infrastructure point to most of this growth being met by renewables.
China does also have ambitious plans in place for its clean energy transition beyond the next few years. These include increasing its solar capacity by 667% between 2025 and 2060, as well as having wind as its primary source of electricity by 2060.
Asia’s Road to Clean Energy
According to the IEA, the world reached a new all-time high in power generation-related emissions in 2022, primarily as a result of the growth in fossil-fuel-generated electricity in the Asia Pacific.
With that said, these emissions are set to plateau by 2025, with a lot of the global growth in renewables and nuclear power being seen in Asia.
Currently, nuclear power is of particular interest in the continent, especially with 2022’s energy crisis highlighting the need for energy independence and security. India, for instance, is set to have an 80% growth in its nuclear electricity generation in the next two years, with Japan, South Korea, and China following suit in increasing their nuclear capacity.
The road ahead also hints at other interesting insights, specifically when it comes to hydropower in Asia. With heatwaves and droughts becoming more and more commonplace as a result of climate change, the continent may be poised to learn some lessons from Europe’s record-low hydropower generation in 2022, diverting its time and resources to other forms of clean energy, like wind and solar.
Whatever the future holds, one thing is clear: with ambitious plans already underway, Asia’s electricity mix may look significantly different within the next few decades.
Energy Shift
Visualizing Copper Production by Country in 2023
Chile and Peru account for one-third of the world’s copper output.

Visualizing Copper Production by Country in 2023
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Copper is considered an essential metal for the clean energy transition because it is a great conductor of electricity.
As a result, governments around the world have been encouraging the construction of new mines, and mining companies have been seeking new projects and acquiring existing mines to meet the growing demand.
In this graphic, we illustrate global copper production in 2023, based on data from the U.S. Geological Survey, Mineral Commodity Summaries, as of January 2024.
Most Copper Comes from South America
Chile and Peru account for one-third of the world’s copper output.
| Country | Region | 2023E Production (Million tonnes) |
|---|---|---|
| 🇨🇱 Chile | South America | 5.0 |
| 🇵🇪 Peru | South America | 2.6 |
| 🇨🇩 Congo (Kinshasa) | Africa | 2.5 |
| 🇨🇳 China | Asia | 1.7 |
| 🇺🇸 United States | North America | 1.1 |
| 🇷🇺 Russia | Europe/Asia | 0.9 |
| 🇦🇺 Australia | Oceania | 0.8 |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | Asia | 0.8 |
| 🇿🇲 Zambia | Africa | 0.8 |
| 🇲🇽 Mexico | North America | 0.7 |
| 🇰🇿 Kazakhstan | Asia | 0.6 |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | North America | 0.5 |
| 🇵🇱 Poland | Europe | 0.4 |
| 🌍 Rest of World | -- | 3.1 |
| World total (rounded) | -- | 21.5 |
Chile is also home to the two largest mines in the world, Escondida and Collahuasi.
Meanwhile, African countries have rapidly increased their production. The Democratic Republic of Congo, for example, transitioned from being a secondary copper producer in the late 1990s to becoming the third-largest producer by 2023.
Part of the growth in copper mining in Africa is attributed to high investment from China. Chinese mining companies represent 8% of Africa’s total output in the mining sector.
Within its territory, China has also seen a 277% growth in copper production over the last three decades.
In the U.S., Arizona is the leading copper-producing state, accounting for approximately 70% of domestic output. Copper is also mined in Michigan, Missouri, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, and Utah.
Energy Shift
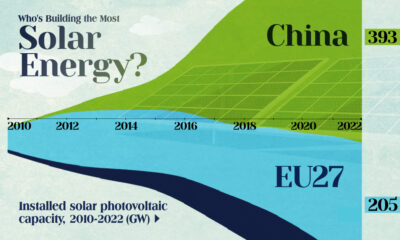
Who’s Building the Most Solar Energy?
China’s solar capacity triples USA, nearly doubles EU.

Who’s Building the Most Solar Energy?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
In 2023, solar energy accounted for three-quarters of renewable capacity additions worldwide. Most of this growth occurred in Asia, the EU, and the U.S., continuing a trend observed over the past decade.
In this graphic, we illustrate the rise in installed solar photovoltaic (PV) capacity in China, the EU, and the U.S. between 2010 and 2022, measured in gigawatts (GW). Bruegel compiled the data..
Chinese Dominance
As of 2022, China’s total installed capacity stands at 393 GW, nearly double that of the EU’s 205 GW and surpassing the USA’s total of 113 GW by more than threefold in absolute terms.
| Installed solar capacity (GW) | China | EU27 | U.S. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 393.0 | 205.5 | 113.0 |
| 2021 | 307.0 | 162.7 | 95.4 |
| 2020 | 254.0 | 136.9 | 76.4 |
| 2019 | 205.0 | 120.1 | 61.6 |
| 2018 | 175.3 | 104.0 | 52.0 |
| 2017 | 130.8 | 96.2 | 43.8 |
| 2016 | 77.8 | 91.5 | 35.4 |
| 2015 | 43.6 | 87.7 | 24.2 |
| 2014 | 28.4 | 83.6 | 18.1 |
| 2013 | 17.8 | 79.7 | 13.3 |
| 2012 | 6.7 | 71.1 | 8.6 |
| 2011 | 3.1 | 53.3 | 5.6 |
| 2010 | 1.0 | 30.6 | 3.4 |
Since 2017, China has shown a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 25% in installed PV capacity, while the USA has seen a CAGR of 21%, and the EU of 16%.
Additionally, China dominates the production of solar power components, currently controlling around 80% of the world’s solar panel supply chain.
In 2022, China’s solar industry employed 2.76 million individuals, with manufacturing roles representing approximately 1.8 million and the remaining 918,000 jobs in construction, installation, and operations and maintenance.
The EU industry employed 648,000 individuals, while the U.S. reached 264,000 jobs.
According to the IEA, China accounts for almost 60% of new renewable capacity expected to become operational globally by 2028.
Despite the phasing out of national subsidies in 2020 and 2021, deployment of solar PV in China is accelerating. The country is expected to reach its national 2030 target for wind and solar PV installations in 2024, six years ahead of schedule.
-

 Electrification3 years ago
Electrification3 years agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe Key Minerals in an EV Battery
-

 Real Assets3 years ago
Real Assets3 years agoThe World’s Top 10 Gold Mining Companies
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoMapped: Solar Power by Country in 2021
-

 Misc3 years ago
Misc3 years agoAll the Metals We Mined in One Visualization
-

 Energy Shift2 years ago
Energy Shift2 years agoWhat Are the Five Major Types of Renewable Energy?
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe World’s Largest Nickel Mining Companies
-

 Misc3 years ago
Misc3 years agoThe Largest Copper Mines in the World by Capacity