Electrification
Visualizing Global EV Production in 2022, by Brand
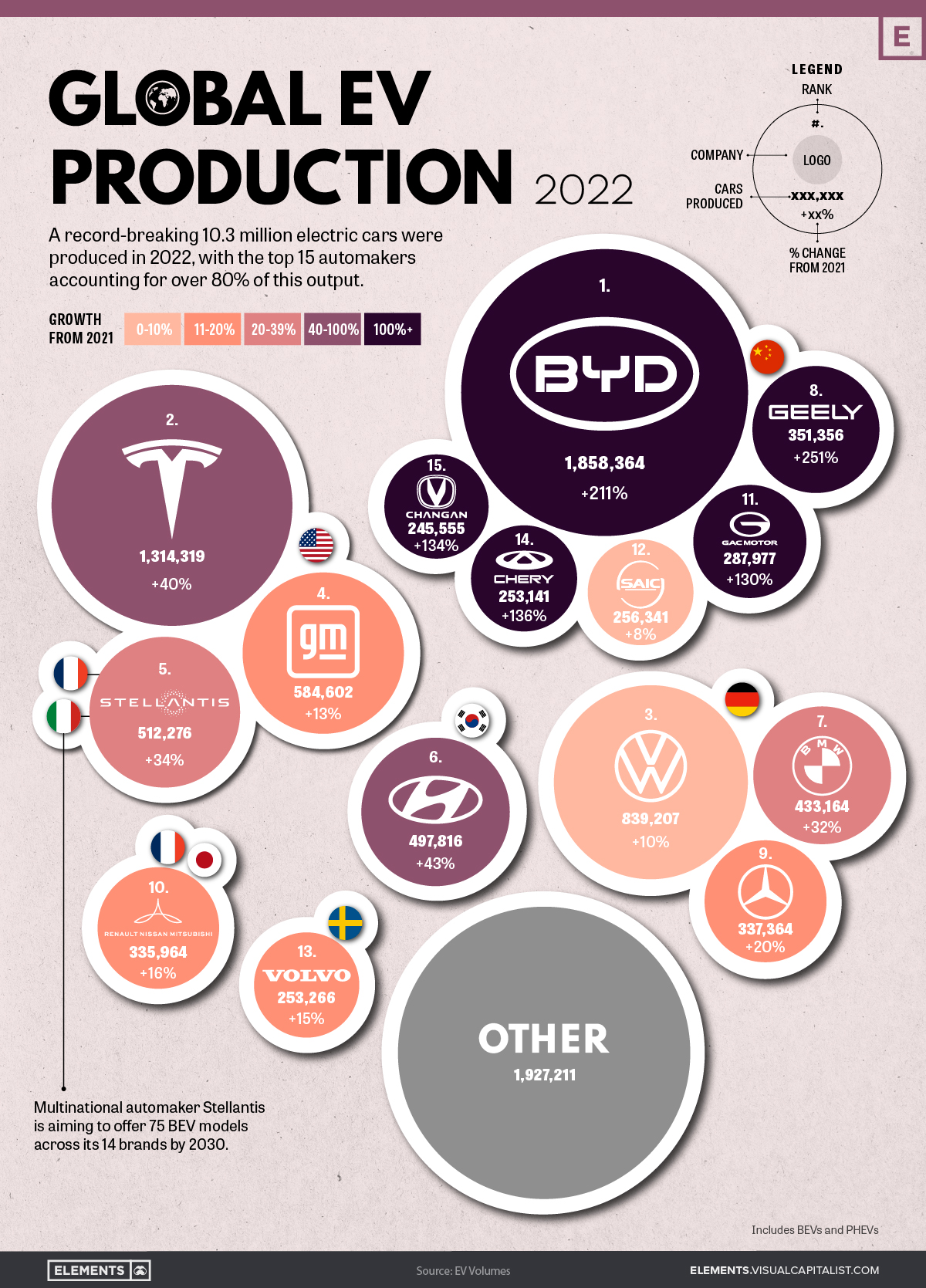
Global EV Production: BYD Surpasses Tesla
2022 was another historic year for EVs, with annual production surpassing 10 million cars for the first time ever. This represents a sizable bump up from 2021’s figure of 6.7 million.
In this infographic, we’ve used data from EV Volumes to visualize the top 15 brands by output. The color of each brand’s bubble represents their growth from 2021, with the darker shades depicting a larger percentage increase.
Data Overview and Key Takeaways
The raw data we used to create this infographic is listed below. Volume figures for 2021 were included for convenience.
| Rank | Company | 2022 | 2021 | Growth from 2021 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇨🇳 BYD | 1,858,364 | 598,019 | 211% |
| 2 | 🇺🇸 Tesla | 1,314,319 | 936,247 | 40% |
| 3 | 🇩🇪 VW Group | 839,207 | 763,851 | 10% |
| 4 | 🇺🇸 GM (incl. Wuling Motors) | 584,602 | 516,631 | 13% |
| 5 | 🇺🇸 🇮🇹 🇫🇷 Stellantis | 512,276 | 381,843 | 34% |
| 6 | 🇰🇷 Hyundai Motors (incl. Kia) | 497,816 | 348,660 | 43% |
| 7 | 🇩🇪 BMW Group | 433,164 | 329,182 | 32% |
| 8 | 🇨🇳 Geely Auto Group | 351,356 | 99,980 | 251% |
| 9 | 🇩🇪 Mercedes-Benz Group | 337,364 | 281,929 | 20% |
| 10 | 🇫🇷 🇯🇵 Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance | 335,964 | 289,473 | 16% |
| 11 | 🇨🇳 GAC Group | 287,977 | 125,384 | 130% |
| 12 | 🇨🇳 SAIC Motor Corp. | 256,341 | 237,043 | 8% |
| 13 | 🇸🇪 Volvo Cars | 253,266 | 220,576 | 15% |
| 14 | 🇨🇳 Chery Auto Co. | 253,141 | 107,482 | 136% |
| 15 | 🇨🇳 Changan Auto Co. | 245,555 | 105,072 | 134% |
| 16 | 🌎 Other (41 companies) | 1,927,211 | 1,326,262 | 45% |
Includes BEVs and PHEVs
BYD Auto
BYD Auto has leaped past Tesla to become the new EV king, boosting its output by a massive 211% in 2022. Given this trajectory, the company will likely become the world’s first automaker to produce over 2 million EVs in a single year.
BYD has a limited presence in non-domestic markets, but this could change rather quickly. The company is planning a major push into Europe, where it expects to build factories in order to avoid EU tariffs on Chinese car imports.
The company is also building a factory in Thailand, to produce right-hand drive models for markets like Australia, New Zealand, and the UK.
Tesla
Tesla increased its output by a respectable 40% in 2022, staying ahead of Western brands like Volkswagen (+10%) and GM (+13%), but falling behind its Chinese rivals such as Geely (+251%).
Whether these Chinese brands can maintain their triple digit growth figures is uncertain, but one thing is clear: Tesla is facing more competition than ever before.
The company is targeting annual production of 20 million cars by 2030, meaning it will need to keep yearly growth rates in the high double digits for the rest of the decade. To support this initiative, Tesla is planning a multi-billion dollar factory in Mexico capable of producing 1 million cars a year.
Hyundai
Hyundai Motor Company, which also owns Kia, posted a similar growth rate to Tesla. The South Korean automaker was a relatively early player in the EV space, revealing the first Hyundai Ioniq in 2016.
In late 2022, several countries including South Korea expressed their disapproval of the Biden administration’s Inflation Reduction Act, which withdrew tax credits on EVs not produced within the United States.
Hyundai is currently building a $5.5 billion EV factory in the state of Georgia, but this facility will not become operational until 2025. In the meantime, South Korea has revised its own EV subsidy program to favor domestic brands.
Electrification
Charted: 4 Reasons Why Lithium Could Be the Next Gold Rush
Visual Capitalist has partnered with EnergyX to show why drops in prices and growing demand may make now the right time to invest in lithium.
4 Reasons Why You Should Invest in Lithium
Lithium’s importance in powering EVs makes it a linchpin of the clean energy transition and one of the world’s most precious minerals.
In this graphic, Visual Capitalist partnered with EnergyX to explore why now may be the time to invest in lithium.
1. Lithium Prices Have Dropped
One of the most critical aspects of evaluating an investment is ensuring that the asset’s value is higher than its price would indicate. Lithium is integral to powering EVs, and, prices have fallen fast over the last year:
| Date | LiOH·H₂O* | Li₂CO₃** |
|---|---|---|
| Feb 2023 | $76 | $71 |
| March 2023 | $71 | $61 |
| Apr 2023 | $43 | $33 |
| May 2023 | $43 | $33 |
| June 2023 | $47 | $45 |
| July 2023 | $44 | $40 |
| Aug 2023 | $35 | $35 |
| Sept 2023 | $28 | $27 |
| Oct 2023 | $24 | $23 |
| Nov 2023 | $21 | $21 |
| Dec 2023 | $17 | $16 |
| Jan 2024 | $14 | $15 |
| Feb 2024 | $13 | $14 |
Note: Monthly spot prices were taken as close to the 14th of each month as possible.
*Lithium hydroxide monohydrate (MB-LI-0033)
**Lithium carbonate (MB-LI-0029)
2. Lithium-Ion Battery Prices Are Also Falling
The drop in lithium prices is just one reason to invest in the metal. Increasing economies of scale, coupled with low commodity prices, have caused the cost of lithium-ion batteries to drop significantly as well.
In fact, BNEF reports that between 2013 and 2023, the price of a Li-ion battery dropped by 82%.
| Year | Price per KWh |
|---|---|
| 2023 | $139 |
| 2022 | $161 |
| 2021 | $150 |
| 2020 | $160 |
| 2019 | $183 |
| 2018 | $211 |
| 2017 | $258 |
| 2016 | $345 |
| 2015 | $448 |
| 2014 | $692 |
| 2013 | $780 |
3. EV Adoption is Sustainable
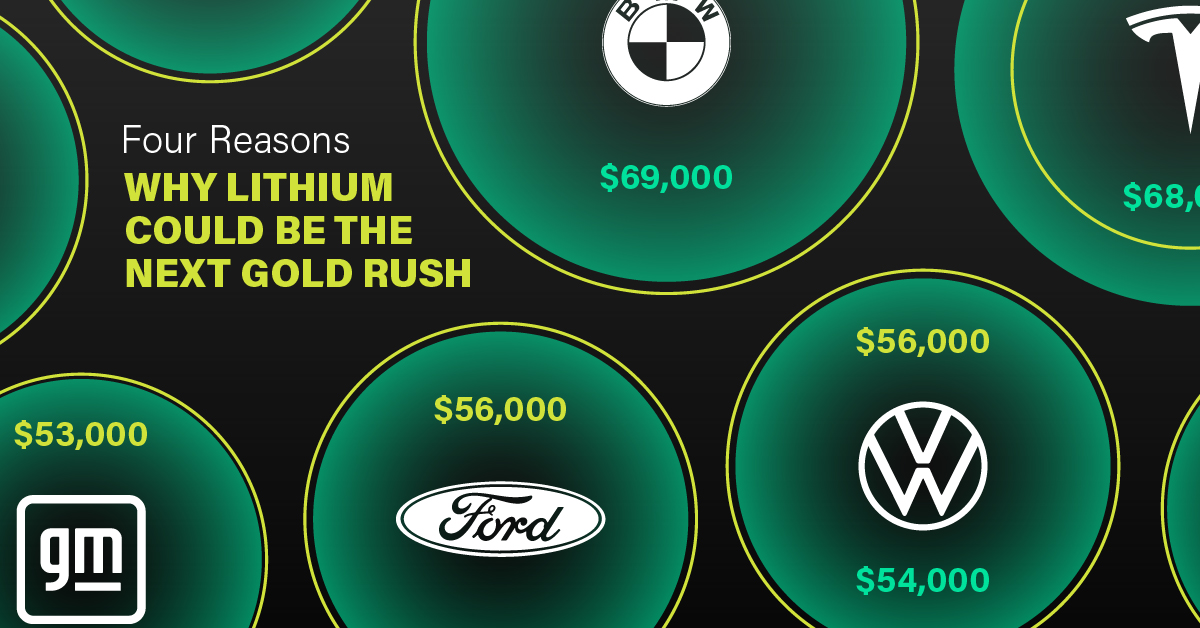
One of the best reasons to invest in lithium is that EVs, one of the main drivers behind the demand for lithium, have reached a price point similar to that of traditional vehicle.
According to the Kelly Blue Book, Tesla’s average transaction price dropped by 25% between 2022 and 2023, bringing it in line with many other major manufacturers and showing that EVs are a realistic transport option from a consumer price perspective.
| Manufacturer | September 2022 | September 2023 |
|---|---|---|
| BMW | $69,000 | $72,000 |
| Ford | $54,000 | $56,000 |
| Volkswagon | $54,000 | $56,000 |
| General Motors | $52,000 | $53,000 |
| Tesla | $68,000 | $51,000 |
4. Electricity Demand in Transport is Growing
As EVs become an accessible transport option, there’s an investment opportunity in lithium. But possibly the best reason to invest in lithium is that the IEA reports global demand for the electricity in transport could grow dramatically by 2030:
| Transport Type | 2022 | 2025 | 2030 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buses 🚌 | 23,000 GWh | 50,000 GWh | 130,000 GWh |
| Cars 🚙 | 65,000 GWh | 200,000 GWh | 570,000 GWh |
| Trucks 🛻 | 4,000 GWh | 15,000 GWh | 94,000 GWh |
| Vans 🚐 | 6,000 GWh | 16,000 GWh | 72,000 GWh |
The Lithium Investment Opportunity
Lithium presents a potentially classic investment opportunity. Lithium and battery prices have dropped significantly, and recently, EVs have reached a price point similar to other vehicles. By 2030, the demand for clean energy, especially in transport, will grow dramatically.
With prices dropping and demand skyrocketing, now is the time to invest in lithium.
EnergyX is poised to exploit lithium demand with cutting-edge lithium extraction technology capable of extracting 300% more lithium than current processes.

Electrification
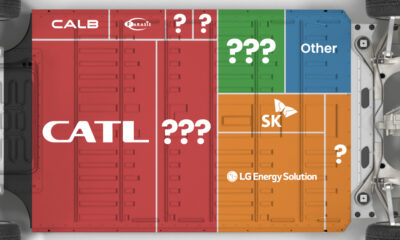
Ranked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
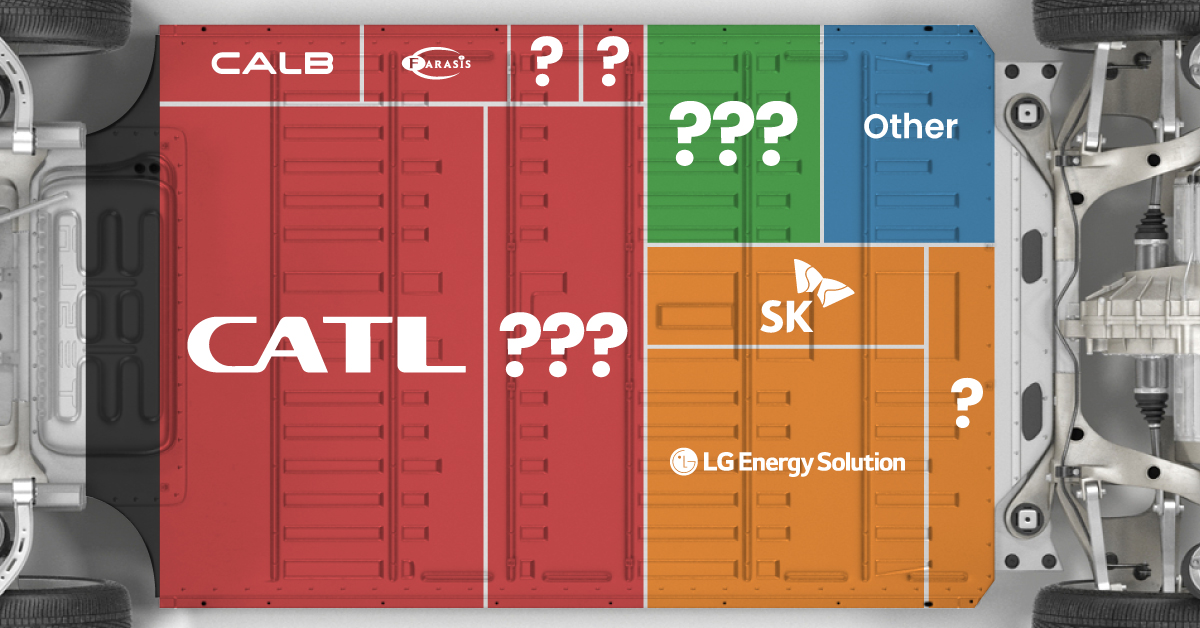
Asia dominates this ranking of the world’s largest EV battery manufacturers in 2023.
The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers in 2023
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Despite efforts from the U.S. and EU to secure local domestic supply, all major EV battery manufacturers remain based in Asia.
In this graphic we rank the top 10 EV battery manufacturers by total battery deployment (measured in megawatt-hours) in 2023. The data is from EV Volumes.
Chinese Dominance
Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL) has swiftly risen in less than a decade to claim the title of the largest global battery group.
The Chinese company now has a 34% share of the market and supplies batteries to a range of made-in-China vehicles, including the Tesla Model Y, SAIC’s MG4/Mulan, and Li Auto models.
| Company | Country | 2023 Production (megawatt-hour) | Share of Total Production |
|---|---|---|---|
| CATL | 🇨🇳China | 242,700 | 34% |
| BYD | 🇨🇳China | 115,917 | 16% |
| LG Energy Solution | 🇰🇷Korea | 108,487 | 15% |
| Panasonic | 🇯🇵Japan | 56,560 | 8% |
| SK On | 🇰🇷Korea | 40,711 | 6% |
| Samsung SDI | 🇰🇷Korea | 35,703 | 5% |
| CALB | 🇨🇳China | 23,493 | 3% |
| Farasis Energy | 🇨🇳China | 16,527 | 2% |
| Envision AESC | 🇨🇳China | 8,342 | 1% |
| Sunwoda | 🇨🇳China | 6,979 | 1% |
| Other | - | 56,040 | 8% |
In 2023, BYD surpassed LG Energy Solution to claim second place. This was driven by demand from its own models and growth in third-party deals, including providing batteries for the made-in-Germany Tesla Model Y, Toyota bZ3, Changan UNI-V, Venucia V-Online, as well as several Haval and FAW models.
The top three battery makers (CATL, BYD, LG) collectively account for two-thirds (66%) of total battery deployment.
Once a leader in the EV battery business, Panasonic now holds the fourth position with an 8% market share, down from 9% last year. With its main client, Tesla, now effectively sourcing batteries from multiple suppliers, the Japanese battery maker seems to be losing its competitive edge in the industry.
Overall, the global EV battery market size is projected to grow from $49 billion in 2022 to $98 billion by 2029, according to Fortune Business Insights.
-

 Electrification3 years ago
Electrification3 years agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe Key Minerals in an EV Battery
-

 Real Assets3 years ago
Real Assets3 years agoThe World’s Top 10 Gold Mining Companies
-

 Misc3 years ago
Misc3 years agoAll the Metals We Mined in One Visualization
-

 Energy Shift2 years ago
Energy Shift2 years agoWhat Are the Five Major Types of Renewable Energy?
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoMapped: Solar Power by Country in 2021
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe World’s Largest Nickel Mining Companies
-
 Electrification3 years ago
Electrification3 years agoHow Much Land is Needed to Power the U.S. with Solar?