Electrification
How Much Land is Needed to Power the U.S. with Solar?
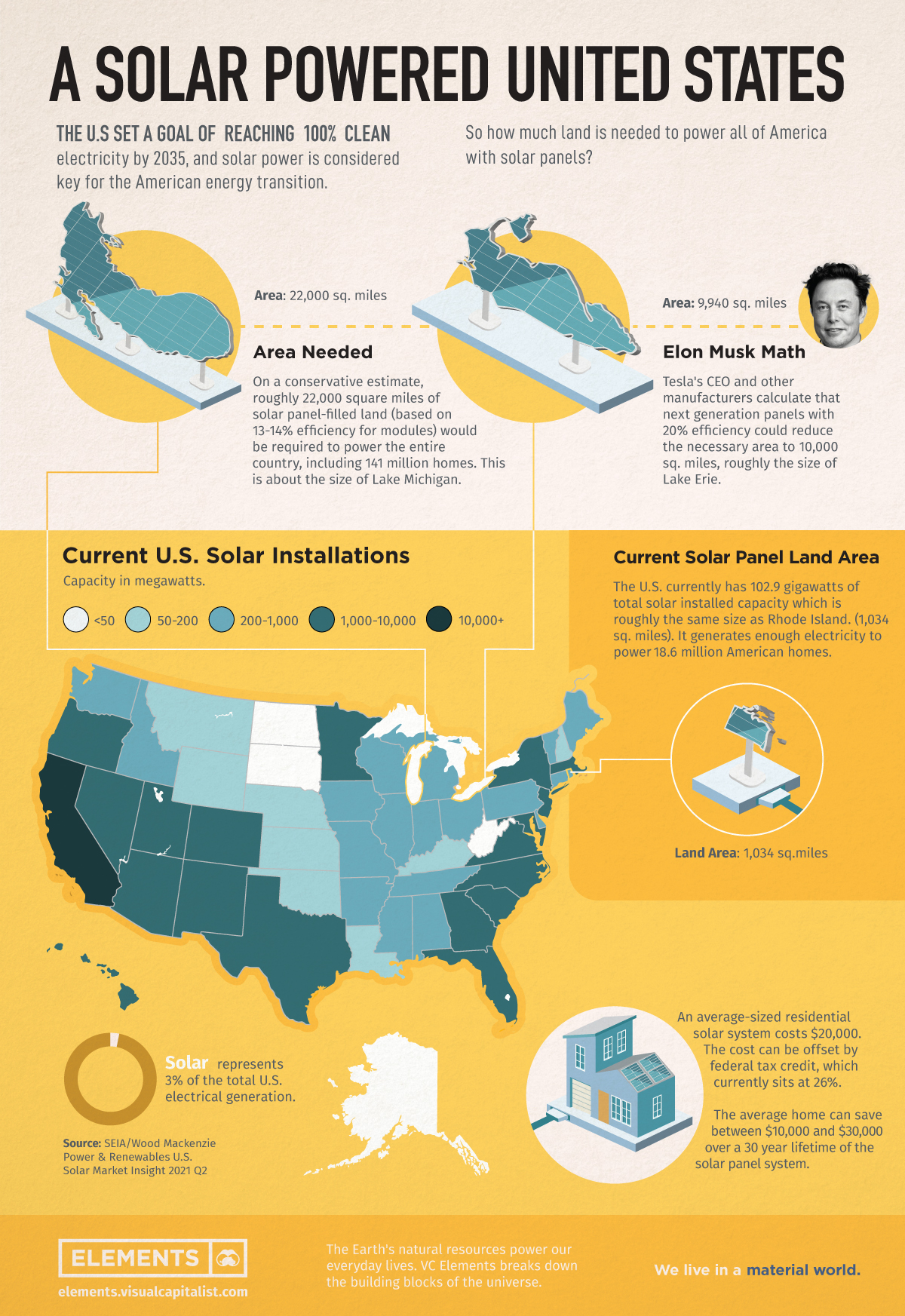
How Much Land is Needed to Power the U.S. with Solar?
The Biden administration has set a goal of reaching 100% clean electricity throughout the U.S. by 2035, and solar power is a key for this American energy transition.
In the last decade alone, solar has experienced an average annual growth rate of 42% in the U.S. thanks to federal tax credits, declining costs, and increasing demand. It is projected that more than one in seven American homes will have a solar power system by 2030.
To put this trend into perspective, this graphic uses data from the United States Department of Energy to see how much land would be needed to power the entire country with solar panels.
Solar Panels Across the Ocean State
The U.S. has 102.9 gigawatts of total solar installed capacity which is equivalent to 965 square miles, roughly the size of the country’s smallest state, Rhode Island. This current solar capacity generates enough electricity to power 18.6 million American homes, which is nearly 13% of the nation’s households.
According to a report from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, roughly 22,000 square miles of solar panel-filled land (about the size of Lake Michigan) would be required to power the entire country, including all 141 million households and businesses, based on 13-14% efficiency for solar modules.
Many solar panels, however, reach 20% efficiency, which could reduce the necessary area to just about 10,000 square miles, equivalent to the size of Lake Erie.
Solar Installations Spreading Across the States
Today, solar represents only 3% of the total U.S. electrical generation.
While California has traditionally dominated the market, other states like Florida and Texas are expanding rapidly, boosted by the residential market.
Large companies with clean energy goals such as Walmart, Apple, Target and Amazon have also helped push solar adoption to near-record levels in 2021.
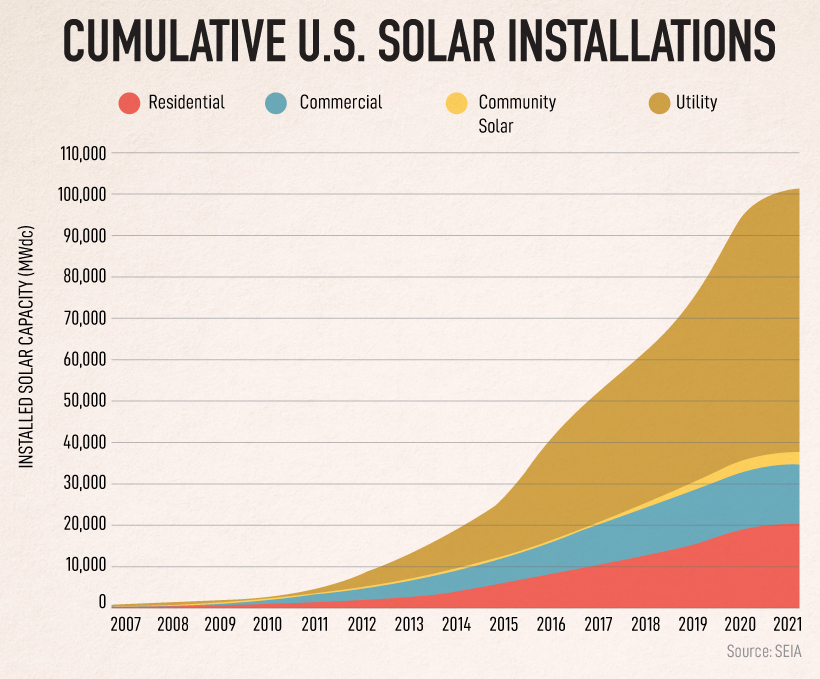
Despite having a high installation cost, the technology tends to bring savings in the long term. An average-sized residential system has dropped from a price of $40,000 in 2010 to roughly $20,000 in 2020. Along with this, solar panels can save between $10,000-$30,000 over a 30-year lifetime.
Between land and rooftops, the United States has more than enough space to build all the solar panels necessary to power the country. Until then, the future of clean electricity will also depend on hydro, nuclear, geothermal, and wind energy.
Electrification
White Gold: Mapping U.S. Lithium Mines
In this graphic, Visual Capitalist partnerered with EnergyX to explore the size and location of U.S. lithium mines.
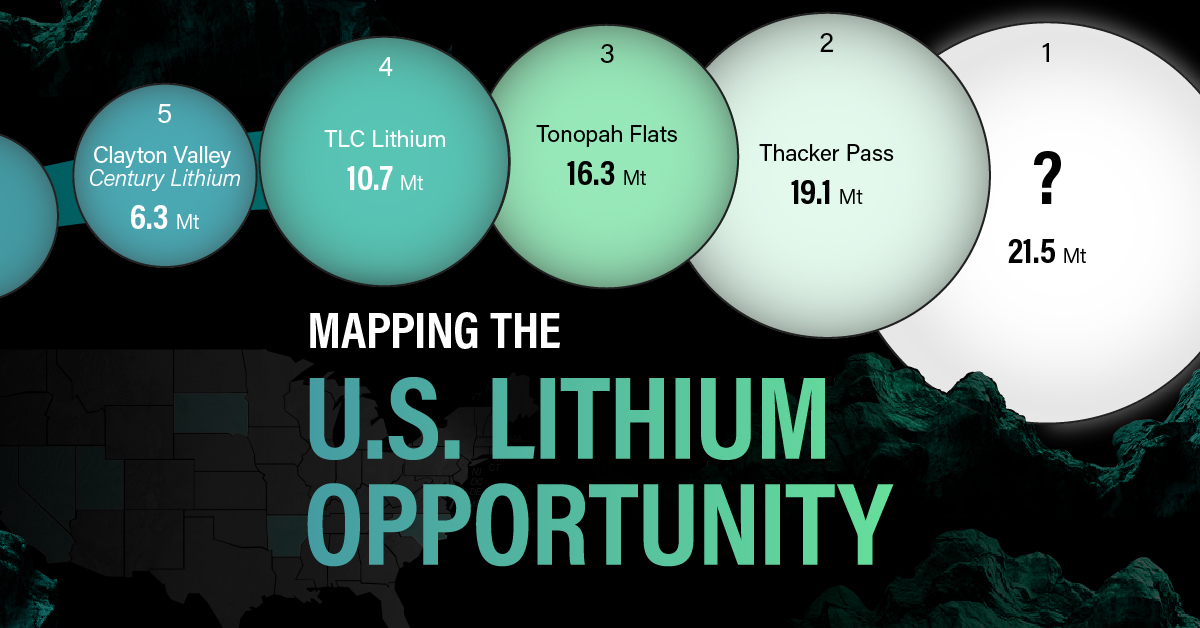
White Gold: Mapping U.S. Lithium Mines
The U.S. doubled imports of lithium-ion batteries for the third consecutive year in 2022, and with EV demand growing yearly, U.S. lithium mines must ramp up production or rely on other nations for their supply of refined lithium.
To determine if the domestic U.S. lithium opportunity can meet demand, we partnered with EnergyX to determine how much lithium sits within U.S. borders.
U.S. Lithium Projects
The most crucial measure of a lithium mine’s potential is the quantity that can be extracted from the source.
For each lithium resource, the potential volume of lithium carbonate equivalent (LCE) was calculated with a ratio of one metric ton of lithium producing 5.32 metric tons of LCE. Cumulatively, existing U.S. lithium projects contain 94.8 million metric tons of LCE.
| Rank | Project Name | LCE, million metric tons (est.) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | McDermitt Caldera | 21.5 |
| 2 | Thacker Pass | 19.1 |
| 3 | Tonopah Flats | 18.0 |
| 4 | TLC Lithium | 10.7 |
| 5 | Clayton Valley (Century Lithium) | 6.3 |
| 6 | Zeus Lithium | 6.3 |
| 7 | Rhyolite Ridge | 3.4 |
| 8 | Arkansas Smackover (Phase 1A) | 2.8 |
| 9 | Basin Project | 2.2 |
| 10 | McGee Deposit | 2.1 |
| 11 | Arkansas Smackover (South West) | 1.8 |
| 12 | Clayton Valley (Lithium-X, Pure Energy) | 0.8 |
| 13 | Big Sandy | 0.3 |
| 14 | Imperial Valley/Salton Sea | 0.3 |
U.S. Lithium Opportunities, By State
U.S. lithium projects mainly exist in western states, with comparatively minor opportunities in central or eastern states.
| State | LCE, million metric tons (est.) |
|---|---|
| Nevada | 88.2 |
| Arkansas | 4.6 |
| Arizona | 2.5 |
| California | 0.3 |
Currently, the U.S. is sitting on a wealth of lithium that it is underutilizing. For context, in 2022, the U.S. only produced about 5,000 metric tons of LCE and imported a projected 19,000 metric tons of LCE, showing that the demand for the mineral is healthy.
The Next Gold Rush?
U.S. lithium companies have the opportunity to become global leaders in lithium production and accelerate the transition to sustainable energy sources. This is particularly important as the demand for lithium is increasing every year.
EnergyX is on a mission to meet U.S. lithium demands using groundbreaking technology that can extract 300% more lithium from a source than traditional methods.
You can take advantage of this opportunity by investing in EnergyX and joining other significant players like GM in becoming a shareholder.

Electrification
Will Direct Lithium Extraction Disrupt the $90B Lithium Market?
Visual Capitalist and EnergyX explore how direct lithium extraction could disrupt the $90B lithium industry.

Will Direct Lithium Extraction Disrupt the $90B Lithium Market?
Current lithium extraction and refinement methods are outdated, often harmful to the environment, and ultimately inefficient. So much so that by 2030, lithium demand will outstrip supply by a projected 1.42 million metric tons. But there is a solution: Direct lithium extraction (DLE).
For this graphic, we partnered with EnergyX to try to understand how DLE could help meet global lithium demands and change an industry that is critical to the clean energy transition.
The Lithium Problem
Lithium is crucial to many renewable energy technologies because it is this element that allows EV batteries to react. In fact, it’s so important that projections show the lithium industry growing from $22.2B in 2023 to nearly $90B by 2030.
But even with this incredible growth, as you can see from the table, refined lithium production will need to increase 86.5% over and above current projections.
| 2022 (million metric tons) | 2030P (million metric tons) | |
|---|---|---|
| Lithium Carbonate Demand | 0.46 | 1.21 |
| Lithium Hydroxide Demand | 0.18 | 1.54 |
| Lithium Metal Demand | 0 | 0.22 |
| Lithium Mineral Demand | 0.07 | 0.09 |
| Total Demand | 0.71 | 3.06 |
| Total Supply | 0.75 | 1.64 |
The Solution: Direct Lithium Extraction
DLE is a process that uses a combination of solvent extraction, membranes, or adsorbents to extract and then refine lithium directly from its source. LiTASTM, the proprietary DLE technology developed by EnergyX, can recover an incredible 300% more lithium per ton than existing processes, making it the perfect tool to help meet lithium demands.
Additionally, LiTASTM can refine lithium at the lowest cost per unit volume directly from brine, an essential step in meeting tomorrow’s lithium demand and manufacturing next-generation batteries, while significantly reducing the footprint left by lithium mining.
| Hard Rock Mining | Underground Reservoirs | Direct Lithium Extraction | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct CO2 Emissions | 15,000 kg | 5,000 kg | 3.5 kg |
| Water Use | 170 m3 | 469 m3 | 34-94 m3 |
| Lithium Recovery Rate | 58% | 30-40% | 90% |
| Land Use | 464 m2 | 3124 m2 | 0.14 m2 |
| Process Time | Variable | 18 months | 1-2 days |
Providing the World with Lithium
DLE promises to disrupt the outdated lithium industry by improving lithium recovery rates and slashing emissions, helping the world meet the energy demands of tomorrow’s electric vehicles.
EnergyX is on a mission to become a worldwide leader in the sustainable energy transition using groundbreaking direct lithium extraction technology. Don’t miss your chance to join companies like GM and invest in EnergyX to transform the future of renewable energy.
-

 Electrification3 years ago
Electrification3 years agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe Key Minerals in an EV Battery
-

 Real Assets3 years ago
Real Assets3 years agoThe World’s Top 10 Gold Mining Companies
-

 Misc3 years ago
Misc3 years agoAll the Metals We Mined in One Visualization
-
 Electrification3 years ago
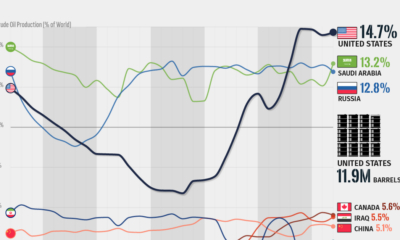
Electrification3 years agoThe Biggest Mining Companies in the World in 2021
-

 Energy Shift2 years ago
Energy Shift2 years agoWhat Are the Five Major Types of Renewable Energy?
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe World’s Largest Nickel Mining Companies
-

 Electrification2 years ago
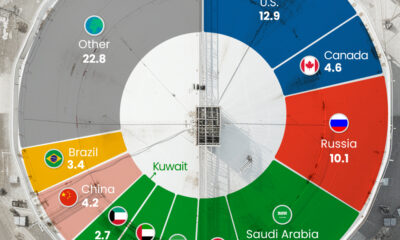
Electrification2 years agoMapped: Solar Power by Country in 2021