Energy Shift
Interactive Map: Crude Oil Pipelines and Refineries of the U.S. and Canada
Mapped: Crude Oil Pipelines and Refineries of the U.S. and Canada
Pipelines are the primary method of transporting crude oil around the world, delivering oil and its derivative products swiftly to refineries and empowering reliant businesses.
And North America is a major oil hub. The U.S. and Canada alone are home to more than 90,000 miles of crude oil and petroleum product pipelines, along with more than 140 refineries that can process around 20 million barrels of oil every day.
This interactive graphic uses data from Rextag to map out crude oil pipelines and refineries across the U.S. and Canada, showcasing individual pipeline diameter and daily refinery throughput.
The Longest Crude Oil Pipeline Networks in North America
Since 2010, U.S. crude oil production has more than doubled from 5.4 million barrels a day to more than 11.5 million. Meanwhile, the pipeline networks needed to transport this newly produced oil have only expanded by roughly 56%.
Today, the largest pipeline network across the U.S. and Canada (with a diameter of at least 10 inches) is the 14,919 mile network managed by Plains, which spans from the northwestern tip of Alberta all the way down to the southern coasts of Texas and Louisiana.
| Company | Length of Crude Oil Pipeline Network |
|---|---|
| Plains Pipeline LP | 14,919 miles |
| Enbridge Energy Partners LP | 12,974 miles |
| Sunoco Inc. | 6,409 miles |
| MPLX LP | 5,913 miles |
| Lotus Midstream | 5,767 miles |
Source: Rextag
Enbridge owns the next largest crude oil pipeline network, with 12,974 miles of crude oil pipelines that are at least 10 inches in diameter. The Canadian company, one of the world’s largest oil companies, transports about 30% of the crude oil produced in North America.
Following the networks of Plains and Enbridge, there’s a steep drop off in the length of pipeline networks, with Sunoco’s crude oil pipeline network spanning about half the length of Enbridge’s at 6,409 miles.
The Largest Crude Oil Refineries in North America
These various sprawling pipeline networks initially carry crude oil to refineries, where it is processed into gasoline, diesel fuel, and other petroleum products.
The refineries with the largest throughput in North America are all located in the Gulf Coast (PADD 3), with the five refineries that process more than 500,000 barrels per day all located in the states of Louisiana and Texas.
| Company | City | Refining Capacity (barrels per day) |
|---|---|---|
| Motiva Enterprises | Port Arthur, Texas | 607,000 |
| Marathon Petroleum | Galveston Bay, Texas | 585,000 |
| Marathon Petroleum | Garyville, Louisiana | 578,000 |
| ExxonMobil | Baytown, Texas | 560,000 |
| ExxonMobil | Baton Rouge, Louisiana | 518,000 |
Source: Rextag
While Texas and Louisiana have six refineries that process more than 400,000 barrels per day, there are only two other facilities outside of these states with the same kind of throughput, located in Whiting, Indiana (435,000 barrels per day) and Fort McMurray, Alberta (465,000 barrels per day).
Fort McMurray’s facility is an upgrader, which differs from refineries as it upgrades heavy oils like bitumen into lighter synthetic crude oil which flows through pipelines more easily. Many oil refineries aren’t able to directly convert bitumen, which is extracted from oil sands like those found in Alberta, making upgraders a necessary part in the production and processing of crude oil from oil sands.
The Uncertain Future of New Pipelines in North America
The development of new pipelines remains a contentious issue in Canada and the U.S., with the cancellation of the Keystone XL pipeline emblematic of growing anti-pipeline sentiment. In 2021, only 14 petroleum liquids pipeline projects were completed in the U.S., which was the lowest amount of new pipelines and expansions since 2013.
But domestic energy production is once again in the spotlight due to the U.S. ban on Russian oil imports and Russia’s impending export ban on raw materials. North American consumers are now facing surging gasoline and energy prices as foreign oil is proving to be far less reliable in times of geopolitical turmoil.
It’s important to note that pipelines are not a perfect solution, as leaks and spills in just the last decade have resulted in billions of dollars of damages. From 2010 to 2020, the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration recorded 983 incidents that resulted in 149,000 spilled and unrecovered barrels of oil, five fatalities, 27 injuries, and more than $2.5B in damages.
But over the past five years, liquid pipeline incidents have fallen by 21% while pipeline mileage and barrels delivered have increased by more than 27%. Along with these infrastructure improvements, pipeline developers and operators emphasize the lack of better alternatives, as freight and seaborne transportation are both far less efficient and result in more carbon emissions.
Currently, pipelines remain key components of energy consumption across the U.S. and Canada, and as global energy markets face supply squeezes, international sanctions, and geopolitical turbulence, the focus on them has grown.
Energy Shift
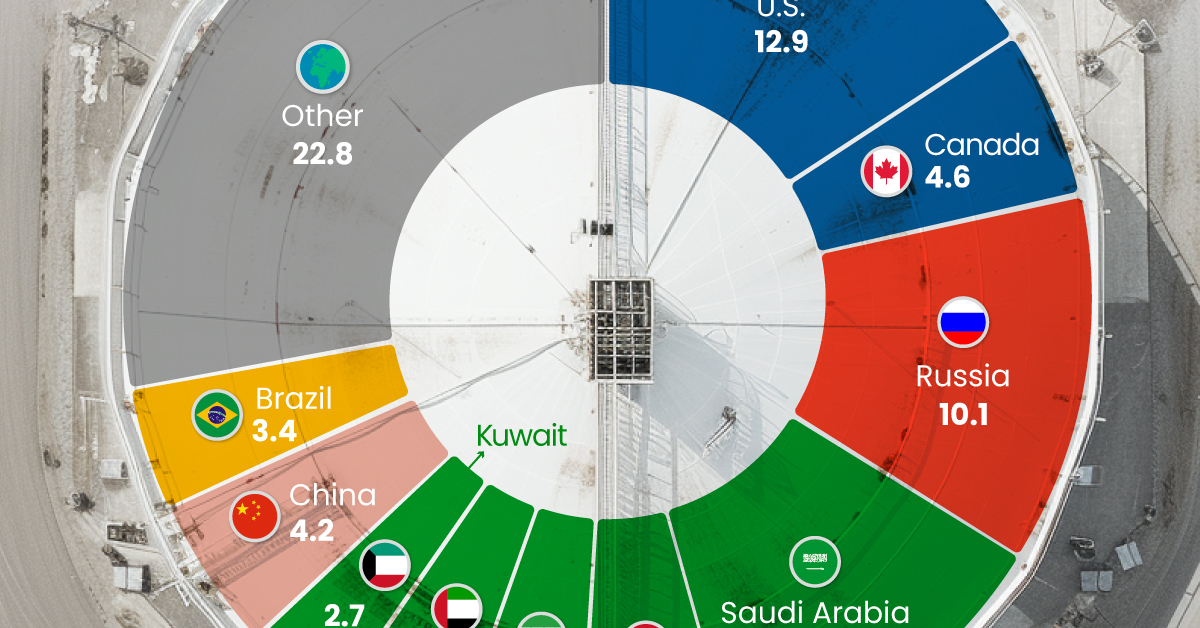
The World’s Biggest Oil Producers in 2023
Just three countries accounted for 40% of global oil production last year.
The World’s Biggest Oil Producers in 2023
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
Despite efforts to decarbonize the global economy, oil still remains one of the world’s most important resources. It’s also produced by a fairly limited group of countries, which can be a source of economic and political leverage.
This graphic illustrates global crude oil production in 2023, measured in million barrels per day, sourced from the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA).
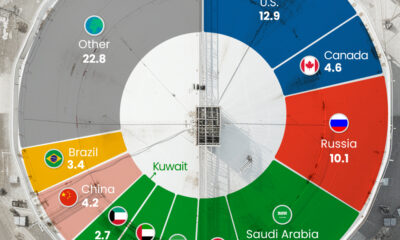
Three Countries Account for 40% of Global Oil Production
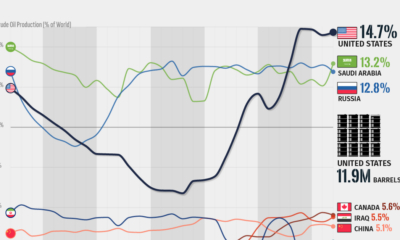
In 2023, the United States, Russia, and Saudi Arabia collectively contributed 32.7 million barrels per day to global oil production.
| Oil Production 2023 | Million barrels per day |
|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 U.S. | 12.9 |
| 🇷🇺 Russia | 10.1 |
| 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | 9.7 |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | 4.6 |
| 🇮🇶 Iraq | 4.3 |
| 🇨🇳 China | 4.2 |
| 🇮🇷 Iran | 3.6 |
| 🇧🇷 Brazil | 3.4 |
| 🇦🇪 UAE | 3.4 |
| 🇰🇼 Kuwait | 2.7 |
| 🌍 Other | 22.8 |
These three nations have consistently dominated oil production since 1971. The leading position, however, has alternated among them over the past five decades.
In contrast, the combined production of the next three largest producers—Canada, Iraq, and China—reached 13.1 million barrels per day in 2023, just surpassing the production of the United States alone.
In the near term, no country is likely to surpass the record production achieved by the U.S. in 2023, as no other producer has ever reached a daily capacity of 13.0 million barrels. Recently, Saudi Arabia’s state-owned Saudi Aramco scrapped plans to increase production capacity to 13.0 million barrels per day by 2027.
In 2024, analysts forecast that the U.S. will maintain its position as the top oil producer. In fact, according to Macquarie Group, U.S. oil production is expected to achieve a record pace of about 14 million barrels per day by the end of the year.
Energy Shift
How Much Does the U.S. Depend on Russian Uranium?
Despite a new uranium ban being discussed in Congress, the U.S. is still heavily dependent on Russian uranium.

How Much Does the U.S. Depend on Russian Uranium?
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
The U.S. House of Representatives recently passed a ban on imports of Russian uranium. The bill must pass the Senate before becoming law.
In this graphic, we visualize how much the U.S. relies on Russian uranium, based on data from the United States Energy Information Administration (EIA).
U.S. Suppliers of Enriched Uranium
After Russia invaded Ukraine, the U.S. imposed sanctions on Russian-produced oil and gas—yet Russian-enriched uranium is still being imported.
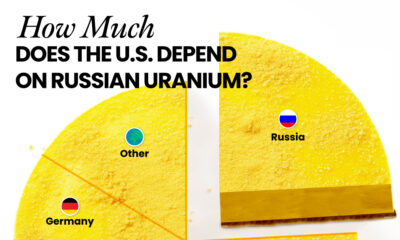
Currently, Russia is the largest foreign supplier of nuclear power fuel to the United States. In 2022, Russia supplied almost a quarter of the enriched uranium used to fuel America’s fleet of more than 90 commercial reactors.
| Country of enrichment service | SWU* | % |
|---|---|---|
| 🇺🇸 United States | 3,876 | 27.34% |
| 🇷🇺 Russia | 3,409 | 24.04% |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 1,763 | 12.40% |
| 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 1,593 | 11.23% |
| 🇳🇱 Netherlands | 1,303 | 9.20% |
| Other | 2,232 | 15.79% |
| Total | 14,176 | 100% |
SWU stands for “Separative Work Unit” in the uranium industry. It is a measure of the amount of work required to separate isotopes of uranium during the enrichment process. Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration
Most of the remaining uranium is imported from European countries, while another portion is produced by a British-Dutch-German consortium operating in the United States called Urenco.
Similarly, nearly a dozen countries around the world depend on Russia for more than half of their enriched uranium—and many of them are NATO-allied members and allies of Ukraine.
In 2023 alone, the U.S. nuclear industry paid over $800 million to Russia’s state-owned nuclear energy corporation, Rosatom, and its fuel subsidiaries.
It is important to note that 19% of electricity in the U.S. is powered by nuclear plants.
The dependency on Russian fuels dates back to the 1990s when the United States turned away from its own enrichment capabilities in favor of using down-blended stocks of Soviet-era weapons-grade uranium.
As part of the new uranium-ban bill, the Biden administration plans to allocate $2.2 billion for the expansion of uranium enrichment facilities in the United States.
-

 Electrification3 years ago
Electrification3 years agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe Key Minerals in an EV Battery
-

 Real Assets2 years ago
Real Assets2 years agoThe World’s Top 10 Gold Mining Companies
-

 Misc3 years ago
Misc3 years agoAll the Metals We Mined in One Visualization
-
 Electrification3 years ago
Electrification3 years agoThe Biggest Mining Companies in the World in 2021
-

 Energy Shift2 years ago
Energy Shift2 years agoWhat Are the Five Major Types of Renewable Energy?
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe World’s Largest Nickel Mining Companies
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoMapped: Solar Power by Country in 2021