Urbanization
Mapped: Air Pollution Levels Around the World in 2022
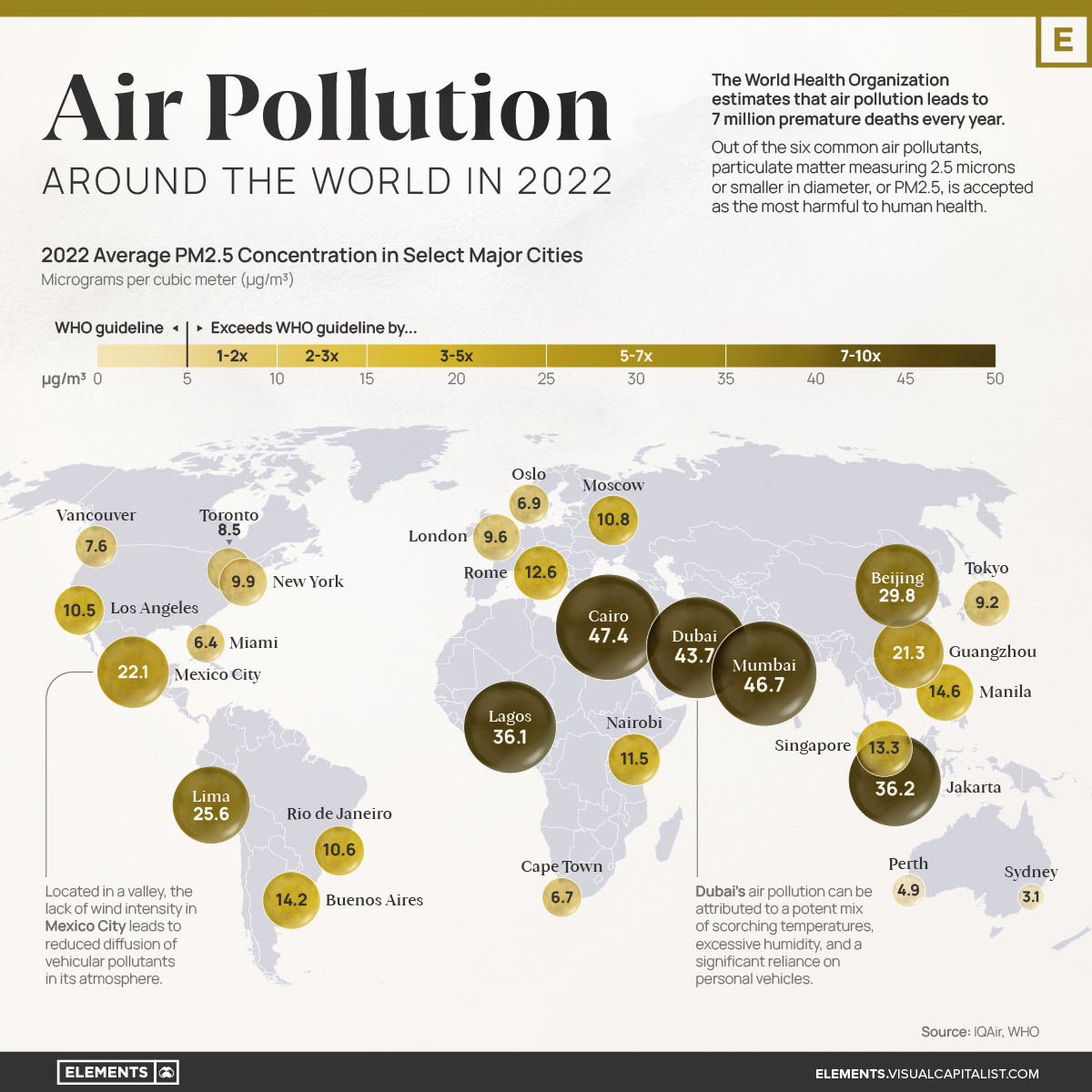
Mapped: Air Pollution Levels Around the World
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that air pollution leads to 7 million premature deaths every year.
Out of the six common air pollutants, particulate matter measuring 2.5 microns or smaller in diameter, or PM2.5, is accepted as the most harmful to human health. This is due to its prevalence in the atmosphere and the broad range of adverse health effects associated with its exposure, such as heart disease, stroke, lung cancer and chronic respiratory diseases.
With that context in mind, this visualization uses IQAir’s World Air Quality Report to map out the 2022 average PM2.5 concentrations in select major cities around the globe, expressed in micrograms per cubic meter (μg/m³).
Understanding the WHO Air Pollution Guidelines
Did you know that in 2019, only 1% of the global population lived in places where WHO global air quality guidelines were met?
Designed to protect public health from the harmful effects of air pollution, the guidelines cover a range of air pollutants, including particulate matter, ozone, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and carbon monoxide.
The healthy limits for PM2.5 are set at an annual average of 0-5 μg/m³.
| WHO Classification | Annual Average PM2.5 Concentration (μg/m³) | % of countries within classification, 2022* |
|---|---|---|
| WHO Air Quality Guideline | 0 - 5 | 9.9% |
| Interim Target 4 | 5.1 - 10 | 18.3% |
| Interim Target 3 | 10.1 - 15 | 19.8% |
| Interim Target 2 | 15.1 - 25 | 28.2% |
| Interim Target 1 | 25.1 - 35 | 9.9% |
| Exceeds Target Levels | 35.1 - 50 | 7.6% |
| Exceeds Target Levels | > 50 | 6.1% |
*Percentages are calculated as a proportion of the 131 countries that had sufficient air quality data and were included in IQAir’s World Air Quality Report in 2022.
According to IQAir’s World Air Quality Report, only 13 countries or territories met the recommended concentration of PM2.5 in 2022. Among them were Australia, Finland, Puerto Rico, Iceland, Bermuda, and Guam.
Above this guideline, many countries fell within the four interim targets, while nearly 14% recorded air pollution levels that exceeded all target levels.
The Effects of Air Quality on Mortality
While it can be a little difficult to grasp what the above concentrations represent, thinking of them in terms of their effect on mortality can shed some light on their significance.
According to the WHO, non-accidental mortality rates multiply by 1.08 per 10 µg/m³ increase in PM2.5 concentration, but only up to 35 μg/m³. Above that, mortality growth rates may not be linear, resulting in many more deaths.
Here is an example to highlight what that means.
- Say that, for a population living within the WHO PM2.5 guideline, the non-accidental mortality rate is arbitrarily set to 100 deaths for a given period.
- If this area’s PM2.5 concentration goes up to 10 μg/m³, putting them at Interim Target 4, they would see 104 deaths in that same amount of time.
- At Interim Target 3, where their PM2.5 concentration would be 15 μg/m³, they would see 108 deaths.
- At Interim Target 2, they’d see 117.
- Finally, at Interim Target 1, they’d see 126.
Beyond Interim Target 1 (above 35 μg/m³), deaths would potentially grow much faster. As of 2022, around 14% of countries report levels above this threshold, including Chad, India, Pakistan, Qatar, and Nigeria.
The State of Air Pollution Around the World
While many cities in North America and Europe have seen steady and relatively lower PM2.5 concentrations during the last few years, many cities (especially those in Asia) have been making strides in lowering their air pollution levels.
Nonetheless, many of them still record PM2.5 concentrations that are more than six times the WHO guideline.
| City | 2022 annual average PM2.5 concentration (μg/m³) | 2018 annual average PM2.5 concentration (μg/m³) |
|---|---|---|
| 🇪🇬 Cairo, Egypt | 47.4 | N/A |
| 🇮🇳 Mumbai, India | 46.7 | 58.6 |
| 🇦🇪 Dubai, UAE | 43.7 | 55.3 |
| 🇮🇩 Jakarta, Indonesia | 36.2 | 45.3 |
| 🇳🇬 Lagos, Nigeria | 36.1 | N/A |
| 🇨🇳 Beijing, China | 29.8 | 50.9 |
| 🇵🇪 Lima, Peru | 25.6 | 28 |
| 🇲🇽 Mexico City, Mexico | 22.1 | 19.7 |
| 🇨🇳 Guangzhou, China | 21.3 | 33.2 |
| 🇵🇭 Manila, Philippines | 14.6 | N/A |
| 🇦🇷 Buenos Aires, Argentina | 14.2 | 12.4 |
| 🇸🇬 Singapore, Singapore | 13.3 | 14.8 |
| 🇮🇹 Rome, Italy | 12.6 | N/A |
| 🇰🇪 Nairobi, Kenya | 11.5 | N/A |
| 🇷🇺 Moscow, Russia | 10.8 | 10.1 |
| 🇧🇷 Rio de Janeiro, Brazil | 10.6 | N/A |
| 🇺🇸 Los Angeles, USA | 10.5 | 14.4 |
| 🇺🇸 New York, USA | 9.9 | N/A |
| 🇬🇧 London, UK | 9.6 | 12 |
| 🇯🇵 Tokyo, Japan | 9.2 | 13.1 |
| 🇨🇦 Toronto, Canada | 8.5 | 7.8 |
| 🇨🇦 Vancouver, Canada | 7.6 | N/A |
| 🇳🇴 Oslo, Norway | 6.9 | 8.2 |
| 🇿🇦 Cape Town, South Africa | 6.7 | N/A |
| 🇺🇸 Miami, USA | 6.4 | 7.8 |
| 🇦🇺 Perth, Australia | 4.9 | N/A |
| 🇦🇺 Sydney, Australia | 3.1 | 7.6 |
Most parts of the world did not meet the annual WHO recommendation for clean and healthy air in 2022.
However, the cost of inaction toward cleaner air is very high. In addition to the millions of premature deaths each year, the global cost of health damages associated with air pollution currently sits at $8.1 trillion.
Unfortunately, things that are integral to our quality of life, such as industrial activities, transportation, energy production, and agricultural practices, are also the leading causes of air pollution around the world.
As such, a multi-faceted approach to lowering pollution is essential to protect lives, especially to benefit those already more vulnerable to poor air quality, such as kids and the elderly.
Urbanization
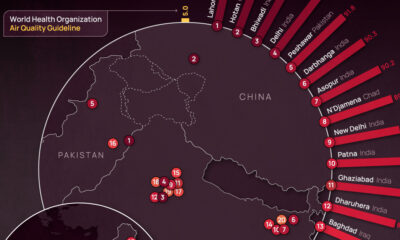
Ranked: The 20 Most Air-Polluted Cities on Earth
Using 2022 average PM2.5 concentrations, we rank the most polluted cities in the world.
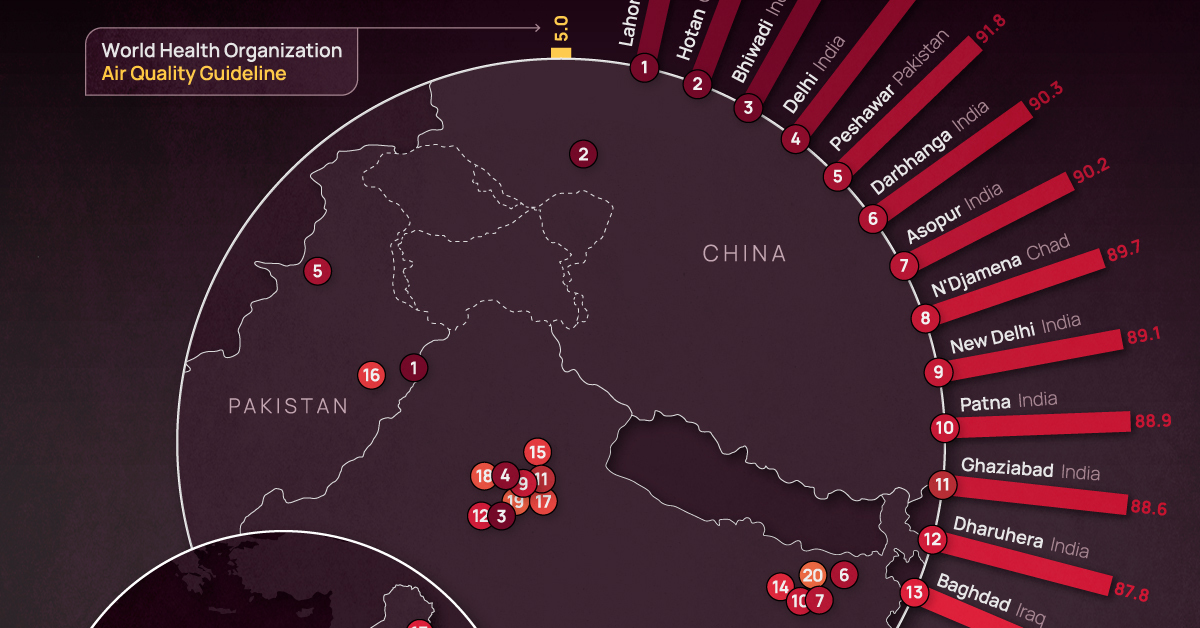
Ranked: The 20 Most Air-Polluted Cities on Earth
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), almost the entire global population (99%) breathes air that exceeds WHO air quality limits.
In the above map, we use 2022 average PM2.5 concentrations from IQAir’s World Air Quality Report to visualize the most air-polluted major cities in the world.
World’s Air Pollution Hot Spots
As one of the standard air quality indicators used by the WHO, the PM2.5 concentration refers to the quantity of fine particulate matter with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less in a given volume of air.
Fine particulate matter that is this small can penetrate the lungs when inhaled and enter the bloodstream, affecting all major organs.
Based on annual average PM2.5 concentrations (μg/m³) in 2022, here are the most polluted cities in the world.
| Rank | City | 2022 average PM2.5 concentration (μg/m³) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇵🇰 Lahore, Pakistan | 97.4 |
| 2 | 🇨🇳 Hotan, China | 94.3 |
| 3 | 🇮🇳 Bhiwadi, India | 92.7 |
| 4 | 🇮🇳 Delhi, India | 92.6 |
| 5 | 🇵🇰 Peshawar, Pakistan | 91.8 |
| 6 | 🇮🇳 Darbhanga, India | 90.3 |
| 7 | 🇮🇳 Asopur, India | 90.2 |
| 8 | 🇹🇩 N'Djamena, Chad | 89.7 |
| 9 | 🇮🇳 New Delhi, India | 89.1 |
| 10 | 🇮🇳 Patna, India | 88.9 |
| 11 | 🇮🇳 Ghaziabad, India | 88.6 |
| 12 | 🇮🇳 Dharuhera, India | 87.8 |
| 13 | 🇮🇶 Baghdad, Iraq | 86.7 |
| 14 | 🇮🇳 Chapra, India | 85.9 |
| 15 | 🇮🇳 Muzaffarnagar, India | 85.5 |
| 16 | 🇵🇰 Faisalabad, Pakistan | 84.5 |
| 17 | 🇮🇳 Greater Noida, India | 83.2 |
| 18 | 🇮🇳 Bahadurgarh, India | 82.2 |
| 19 | 🇮🇳 Faridabad, India | 79.7 |
| 20 | 🇮🇳 Muzaffarpur, India | 79.2 |
With numbers these high, the concentration of some or all of the following pollutants are at dangerous levels in these cities:
- Ground-level ozone
- Particulate matter
- Carbon monoxide
- Sulfur dioxide
- Nitrogen dioxide
At the top of the list, Lahore in Pakistan has a combination of high vehicle and industrial emissions, as well as smoke from brick kilns, crop residue, general waste burning, and dust from construction sites.
Air pollution levels can also be impacted by practices such as large-scale tree removal in order to build new roads and buildings.
As a result of its growing population and rapidly expanding industrial sector, India has 14 cities on the list, outpacing China, formerly considered the world’s number one air pollution source.
The only African country on the list, Chad, experienced severe dust storms in 2022 that resulted in an 18% increase in PM2.5 concentration in 2022 compared to the previous year.
The Cost of Poor Air Quality
Poor air quality is one of the leading causes of early deaths worldwide, just behind high blood pressure, tobacco use, and poor diet.
According to a 2020 study by the Health Effects Institute, 6.67 million people died as a result of air pollution in 2019.
In addition to the millions of premature deaths each year, the global cost of health damages associated with air pollution currently sits at $8.1 trillion.
Urbanization
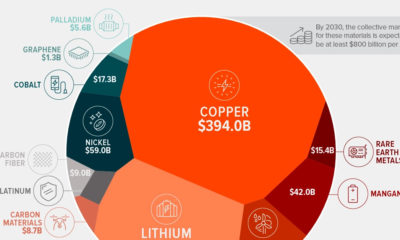
Visualizing the World’s Largest Steel-Producing Countries
China has dominated global steel production the past few decades, but how did the country get here, and is its production growth over?

The Largest Steel-Producing Countries: Visualized
Steel is a critical component of modern industry and economy, essential for the construction of buildings, automobiles, and many other appliances and infrastructure used in our daily lives.
This graphic uses data from the World Steel Association to visualize the world’s top steel-producing countries, and highlights China’s ascent to the top, as it now makes up more than half of the world’s steel production.
The State of Global Steel Production
Global steel production in 2022 reached 1,878 million tonnes, barely surpassing the pre-pandemic production of 1,875 million tonnes in 2019.
| Country | 2022 Production (in million tonnes) | Annual Production Change | Global Share |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🇨🇳 China | 1013.0 | -2.0% | 53.9% |
| 🇮🇳 India | 124.8 | 5.3% | 6.6% |
| 🇯🇵 Japan | 89.2 | -7.9% | 4.8% |
| 🇺🇸 United States | 80.5 | -6.5% | 4.3% |
| 🇷🇺 Russia | 71.5 | -5.8% | 3.8% |
| 🇰🇷 South Korea | 65.9 | -6.9% | 3.5% |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 36.8 | -8.8% | 2.0% |
| 🇹🇷 Türkiye | 35.1 | -15.0% | 1.9% |
| 🇧🇷 Brazil | 34.0 | -6.5% | 1.8% |
| 🇮🇷 Iran | 30.6 | 6.8% | 1.6% |
| 🇮🇹 Italy | 21.6 | -13.0% | 1.1% |
| 🇹🇼 Taiwan | 20.7 | -12.1% | 1.1% |
| 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 20.0 | -15.0% | 1.1% |
| 🇲🇽 Mexico | 18.2 | -1.9% | 1.0% |
| 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 15.6 | 8.3% | 0.8% |
| Rest of World | 201.0 | -11.2% | 10.7% |
| World Total | 1878.5 | -3.9% | 100.0% |
2022’s steel production marked a significant reduction compared to the post-pandemic rebound of 1,960 million tonnes in 2021, with a year-over-year decline of 4.2%–the largest drop since 2009, and prior to that, 1991.
This decline was spread across many of the world’s top steel producers, with only three of the top fifteen countries, India, Iran, and Indonesia, increasing their yearly production. Most of the other top steel-producing countries saw annual production declines of more than 5%, with Turkey, Italy, Taiwan, and Vietnam’s production all declining by double digits.
Even the world’s top steel-producing nation, China, experienced a modest 2% decline, which due to the country’s large production amounted to a decline of 19.8 million tonnes, more than many other nations produce in a year.
Despite India, the world’s second-largest steel producer, increasing its production by 5.3%, the country’s output still amounts to just over one-tenth of the steel produced by China.
China’s Meteoric Rise in Steel Production
Although China dominates the world’s steel production with more than a 54% share today, this hasn’t always been the case.
In 1967, the World Steel Association’s first recorded year of steel production figures, China only produced an estimated 14 million tonnes, making up barely 3% of global output. At that time, the U.S. and the USSR were competing as the world’s top steel producers at 115 and 102 million tonnes respectively, followed by Japan at 62 million tonnes.
Almost three decades later in 1996, China had successively overtaken Russia, the U.S., and Japan to become the top steel-producing nation with 101 million tonnes of steel produced that year.
The early 2000s marked a period of rapid growth for China, with consistent double-digit percentage increases in steel production each year.
The Recent Decline in China’s Steel Production
Since the early 2000s, China’s average annual growth in steel production has slowed to 3.4% over the last decade (2013-2022), a considerable decline compared to the previous decade’s (2003-2012) 15.2% average annual growth rate.
The past couple of years have seen China’s steel production decline, with 2021 and 2022 marking the first time the country’s production fell for two consecutive years in a row.
While it’s unlikely China will relinquish its position as the top steel-producing nation anytime soon, it remains to be seen whether this recent decline marks the beginning of a new trend or just a brief deviation from the country’s consistent production growth.
-

 Electrification3 years ago
Electrification3 years agoRanked: The Top 10 EV Battery Manufacturers
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe Key Minerals in an EV Battery
-

 Real Assets3 years ago
Real Assets3 years agoThe World’s Top 10 Gold Mining Companies
-

 Misc3 years ago
Misc3 years agoAll the Metals We Mined in One Visualization
-
 Electrification3 years ago
Electrification3 years agoThe Biggest Mining Companies in the World in 2021
-

 Energy Shift2 years ago
Energy Shift2 years agoWhat Are the Five Major Types of Renewable Energy?
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoMapped: Solar Power by Country in 2021
-

 Electrification2 years ago
Electrification2 years agoThe World’s Largest Nickel Mining Companies